In this Article, we covered everything there is to know about the Ukraine-Russia conflict. Learn more about the war between Russia and Ukraine, the Russia Ukrainian crisis, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Tensions on Ukraine’s border with Russia are at an all-time high. The Civil Services Examination’s International Relations section includes the Ukrainian Crisis. It’s one of the IAS exam’s most important topics. As a result, read the entire article.
Introduction
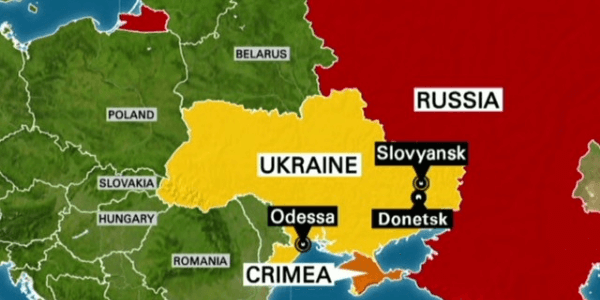
The tensions along the Russia-Ukraine border are a considerable security threat to the region, with the potential to escalate into a larger confrontation. According to Ukraine, Russia has gathered over 90,000 troops on the border, and US intelligence sources suggest that a Russian invasion of Ukraine might happen as soon as next month.
Russia has demonstrated its willingness to intervene militarily in Ukraine as recently as 2014. In that year, Russia annexed Crimea from Ukraine, marking the first time since World War II that a European country had taken territory from another. Here is a link to some Free UPSC Study Materials.
24th February Recent Updates
- Russia stated on February 24 that it had destroyed 74 Ukrainian military facilities, including 11 airbases. During the two countries’ military confrontation, Russian shelling has killed 40 Ukrainian soldiers and ten civilians. Meanwhile, Ukraine claimed to have killed approximately 50 Russian occupiers but provided no details.
- Russia’s invasion of Ukraine began early Thursday morning, following President Putin’s proclamation. Following this, explosions were recorded in various places, and air sirens sounded in Kyiv, signifying that the city was under attack. Ukraine’s capital is Kyiv.
- Ukraine has severed diplomatic relations with Russia, according to President Volodymyr Zelenskiy, after Russia launched an all-out invasion of the country by land, air, and sea, the worst offensive carried out by one European state against another since World War II. In the midst of this, President Zelenskiy declared martial law in the country, and Ukraine’s Foreign Minister threatened to fight Russia.
- US President Joe Biden imposed harsh penalties against Russia, aiming at cutting off Russia’s main banks and blocking the country from acquiring crucial US technologies for its defense, aerospace, and maritime industries.
- Meanwhile, Australia has encouraged Russia to back down, China has urged all parties to exercise caution, Japan has criticized Russia, and Britain is set to impose penalties on Russia.
- Given the severe circumstances in the region, a special Air India jet is on its way to Ukraine to evacuate Indians. India has authorized extra flights to evacuate its citizens. Previously, only three flights were scheduled on 22nd, 24 & 26 February.
Let us discuss the conflict between Ukraine and Russia. Learn more about the Russian-Ukrainian war, the Russia-Ukraine crisis, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine.

Ukraine Russia Crisis
Russia is a country that has a long history. The situation in Ukraine represents a serious security problem in the Eurasian region, with the potential to spiral out of control. In terms of geopolitics, it could exacerbate the worsening of Russia’s relations with the United States and Europe. To India, the Ukraine conflict in the heart of Europe may appear distant. However, it has far-reaching implications not only for India’s relations with the United States, the European Union, Russia, and China but also for the greater geopolitical dynamic in Asia.
For hundreds of years, Ukraine and Russia have shared cultural, linguistic, and familial links. For many Russians and ethnic Russians in Ukraine, the joint heritage of the two countries is an emotional topic that has been exploited for electoral and military goals. Ukraine was the second-most powerful republic in the Soviet Union after Russia, and it played an important geopolitical, economic, and cultural role.
The Beginnings of the Russia Ukrainian Crisis
- In a word, the Ukrainian crisis is a power struggle between Ukraine’s numerous political forces. Among these factions, one favors deeper links with the European Union, while the other desires better relations with Russia.
- Ukraine was one of the Soviet Union’s founding nations, with its farmlands contributing significantly to the Union’s economic production from 1920 until 1991.
- On November 21, 2013, Ukrainian President Victor Yanukovych canceled an agreement with the European Union, escalating the conflict. It sparked a wave of demonstrations from supporters of the accord with the European Union.
- Yanukovych was deposed as president of Ukraine in February 2014 as a result of the succeeding Ukrainian Revolution.
- This, in turn, triggered a wave of protest in Ukraine’s eastern and southern areas, where residents were more supportive of Yanukovych & his pro-Russian policies. Soon after, a political crisis engulfed Ukraine, with pro-European Union and pro-Russian forces vying for control of the country.
- In this context, Russia launched its troops to seize Ukraine’s Crimean peninsula in March 2014. Russia’s casus belli (an act or event that causes or justifies war) was that it was defending its Black Sea port access in case the political turmoil in Ukraine disrupted its trade in the region.
- The Russian incursion reinforced pro-Russian groups in Ukraine, converting simmering dissatisfaction into a full-fledged conflict against Ukraine’s post-revolutionary government.
- In eastern Ukraine, the armed confrontation between the Ukrainian army and Russian-backed rebels raged on from 2014 to 2018. More than 10,000 people died as a result of the war.
After discussing the Russia Ukrainian crisis, let’s talk about the Conflict between Ukraine & Russia.

What is the conflict between Ukraine and Russia?
Major Cause of Conflict:
- Power Balance: Since Ukraine’s breakup from the Soviet Union, Russia and the West have competed for more influence in the nation in order to maintain the region’s power balance in their favor.
- Western Countries’ Buffer Zone: For the United States and the European Union, Ukraine acts as a crucial buffer between Russia and the West. The US and the European Union are getting more determined to keep Ukraine out of Russian hands as tensions with Russia rise.
- Russian Interest in the Black Sea: The Black Sea region’s distinctive terrain provides Russia with significant strategic benefits.
- Protests in Ukraine: Euromaidan Movement (European Square) was a wave of demonstrations and civil disturbances in Ukraine that began in November 2013 with public protests at Kyiv’s Maidan (“Independence Square”). The demonstrations were spurred. For the United States & the European Union, Ukraine acts as a crucial buffer between Russia and the West. The US and the European Union are getting more determined to keep Ukraine out of Russian hands as tensions with Russia rise. As tensions with Russia escalate, the US and the European Union are becoming more eager to keep Ukraine out of Russian hands. By the Ukrainian government’s decision to postpone signing an association agreement with the European Union in favour of deeper ties with Russia and the Eurasian Economic Union
- Separatist Movement: Since 2014, a pro-Russian separatist movement has been active in eastern Ukraine’s Donbas area (Donetsk and Luhansk).
Invasion of Crimea:
Russia captured Crimea from Ukraine, marking the first time since World War II that a European country claimed territory from another.
The Russian military operation in Crimea in the aftermath of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution, which was part of greater upheaval in southern and eastern Ukraine, resulted in the annexation of Crimea from Ukraine.
As a result of its invasion & subsequent annexation of Crimea, Russia now possesses a maritime advantage in the region.
Ukraine’s NATO Membership:
Ukraine has requested that the (NATO) North Atlantic Treaty Organization expedite its country’s membership.
Russia has dubbed such a move a “red line,” fearful of the ramifications of US-led military alliances encroaching on its borders.
Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Turkey, Russia, and Ukraine all border the Black Sea. All of these nations are NATO members.
The Black Sea has become a key zone and a potential maritime flashpoint as a result of the standoff between NATO members and Russia.
Minsk Agreements:
MINSK 1:
- In September 2014, Ukraine and rebels supported by Russia reached an agreement on a 12-point ceasefire in Belarus’ capital.
- It includes provisions for prisoner exchanges, humanitarian relief delivery, and the removal of heavy armaments.
- The arrangement immediately fell apart, with both parties breaking it.
MINSK 2:
- In February 2015, in Minsk, representatives from Russia, Ukraine, the Organization for Security & Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), & the leaders of two pro-Russian separatist regions signed a 13-point accord.
- At the same moment, the leaders of France, Germany, Russia, and Ukraine assembled and issued a statement of support for the agreement.
India’s Position
- India did not join the Western powers in condemning Russia’s incursion in Crimea and maintained a low profile on the subject.
- India voted against a UN resolution proposed by Ukraine condemning alleged human rights breaches in Crimea in November 2020, so siding with old ally Russia on the matter.

What was the reason for the Russian Invasion of Ukraine?
To comprehend the reasons for Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, we must go back to the Cold War era. During Josef Stalin’s leadership, the Soviet Union dispatched ethnic Russians to Ukraine’s eastern regions. This was done to cement Soviet dominance in Ukraine and substantially stifle any local liberation movements that could arise. As a result, Russia’s President had the justification he needed to deploy his force to Ukraine, knowing that he would find support for his actions there. Instead, this assault boosted the pro-Russian camp and helped Yanukovych to return to Kyiv.
Russia saw Ukraine’s determination to open its markets to the EU and collaborate with US corporations to exploit its natural gas deposits as major economic threats. With the ongoing crisis in Ukraine, ties between the US and Russia have continued to worsen since then. Efforts to establish a diplomatic agreement have been unsuccessful. Instead, the battle continues, with daily skirmishes between the two Ukrainian sides and Russian soldiers.
In the same way, World War II began in Europe. When Germany invaded Poland in 1939. to learn more, Go Here.

Conclusion – Ukraine Russia War
In this article, You’ll learn everything you need to know about the Russia and Ukraine conflict, Russia Ukrainian crisis, Russian invasion of Ukraine, and other important aspects of the UPSC exam. Therefore Reviving the Minsk peace process is a possible answer for the situation. As a result, the West (the United States and other western countries) should press both sides to resume discussions and honor their promises under the Minsk accord in order to restore relative peace along the border.
FAQ – Ukraine Russia War
Ukraine is Europe’s second-largest country by area (about 233,062 square miles), after Russia.
Russia attacked and annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine in February and March 2014. This incident occurred in the aftermath of the Dignity Revolution and is part of the larger Russo-Ukrainian conflict.
Following WWII, the western section of Ukraine joined with the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, bringing the entire country (rather than just the eastern half) into the Soviet Union. Following the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, Ukraine regained its independence.
Editor’s Note | Ukraine Russia War
Get all information related to the Ukraine- Russia conflict, The Russia Ukrainian crisis, and The Russian invasion of Ukraine for the UPSC examination. We also have discussed the Invasion of Crimea, Ukraine’s NATO membership, and their Minsk agreements. Later, we have added a UPSC study material link that will assist you in covering all of the major exam topics. You will be able to reach your objectives if you plan well. We wish you success in your exams.