Starlink recently lost 40 satellites after being caught in a geomagnetic storm the day after they were launched. This article will go into better detail on Geo magnetic Storms (Space Storms). We shall talk about what geomagnetic storms are and What exactly are the effects of solar storms? Causes and additional details. The knowledge gained will be beneficial in Geography of GS Paper-1 of the UPSC IAS Exam.
What is Geomagnetic Storm?
- A magnetic storm, also called a geomagnetic storm, is a short disruption in the magnetosphere of the Earth. The magnetosphere protects our planet by acting as a shied. Also, insulating it from harmful solar and cosmic particle radiation along with solar wind erosion. (The continuous flow of charged particles from the Sun).
- It is a huge disturbance of the Earth’s magnetosphere caused by the effective interchange of energy from the solar wind into the space environment around the Earth.
- The magnetosphere shields our planet from destructive solar and cosmic particle radiation, as well as the solar wind—the steady flow of charged particles pouring off the Sun—which erodes the atmosphere.
- These storms are caused by variations in the solar wind, which cause significant changes in the currents, plasma, and fields in the Earth’s magnetosphere.
- Sustained (for several to several hours) periods of high-speed solar wind and, most crucially, a southern directed solar wind magnetic field near the dayside of the magnetosphere is efficient for creating geomagnetic storms.
- This situation is efficient in transferring energy from the solar wind into the Earth’s magnetosphere.
- The most severe storms induced by these conditions are linked to solar Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs). Which occur when a billion tonnes or so of plasma from the Sun, along with its embedded magnetic field, arrives on Earth.
- Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are enormous plasma and magnetic field ejections from the Sun’s corona (outermost layer).
Why in News?
- Elon Musk’s Starlink recently lost dozens of satellites that were caught in a geomagnetic storm a day after launch.
- The loss of more than 40 satellites in a single solar outburst has been termed as “unprecedented” and “massive.” however, The satellites, on the other hand, were meant to burn up upon re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere resulting in no trash in orbit.
What is Starlink?
- Starlink is a SpaceX project that aims to create a broadband network comprised of thousands of orbiting spacecraft.
- The Starlink satellites are equipped with Hall thrusters. which generate an impulse using electricity and krypton gas. They are used to maneuver in orbit, maintain altitude, & guide the spacecraft back into the atmosphere at the end of their mission.
- The Starlink network is one of the numerous active projects aimed at transmitting data signals from space.
The link below can help you learn more about related geography topics. You’ll find everything you need to know about Biogeochemical Cycles here. It is essential for the UPSC examination.

Geomagnetic Storm: Causes
- The magnetic storm could be triggered by a less severe Co-rotating Interaction Region (CIR), which is a high-speed portion of solar wind coming from a coronal hole or Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- The magnetic field of the solar wind clashes with the Earth’s magnetic field, releasing more energy into the magnetosphere.
- Both interactions increase plasma mobility and electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere (owing to greater electric fields inside the magnetosphere).
- During the primary phase of a geomagnetic storm, an electric current in the magnetosphere exerts a magnetic pull that pushes the magnetosphere-solar wind barrier outward.
What is Solar Storm?
Solar storms occur when the Sun generates high-energy bursts in the form of solar flares and coronal mass ejections. These processes deliver a high-speed torrent of electrical charges and magnetic fields toward the Earth.
Solar storms are classified as follows:
- Solar Flares: A solar flare is a quick flash of heightened brightness on the Sun, which is usually seen on its surface and near a sunspot group.
- A geomagnetic storm: it is a short–term disruption of the Earth’s magnetosphere induced by a solar wind shock that interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Coronal Mass Ejection: A coronal mass ejection is a large burst of plasma and magnetic field from the solar corona. They are frequently seen after solar flares and are usually present during a solar prominence eruption.
- Solar Particle Events: When particles (mostly protons) generated by the Sun are driven near the Sun during a flare. A solar particle event (SPE) or prompt proton event (PPE) occurs in interplanetary space by coronal mass ejection shocks.
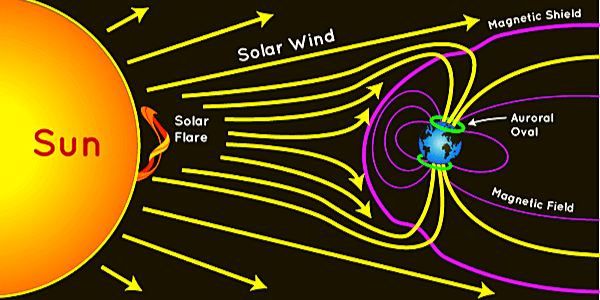
How does Geomagnetic Storm Effects Earth?
The following are the primary and minor impacts (effects) observed on Earth during solar storms (Space Storm):
Can Have an Effect on Space Weather:
Solar flares/ space storms, Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs), high-speed solar winds, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) that come close to Earth can all have an effect on space weather in near-Earth space and the upper atmosphere.
Can Affect Space-Related Services’ Operations:
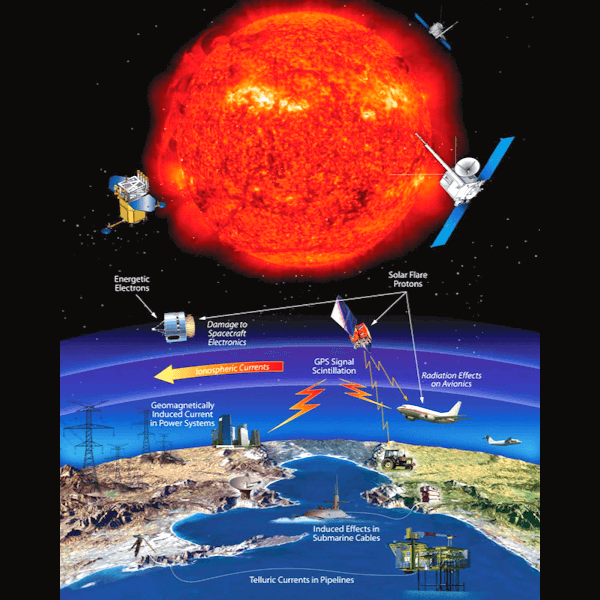
Solar storms have the potential to disrupt space-based services such as GPS, radio, and satellite communication. Flights, electricity networks, and space exploration projects are all at risk.
Geomagnetic storms Can Potentially Effect Magnetosphere Disturbances:
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), which send matter-laden projectiles hurtling across space at millions of kilometers per hour, have the potential to disrupt the magnetosphere, the Earth’s protective barrier. As a result, astronauts on spacewalks may be exposed to solar radiation beyond the Earth’s protective atmosphere, putting their health at risk.
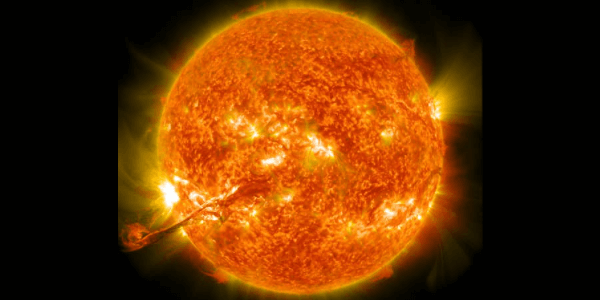
Prediction of Solar Storm
- A solar storm or geomagnetic is the name given to the atmospheric effects that occur on Earth as a result of specific events on the Sun’s surface. Solar storms can be forecast using the following criteria:
- Solar physicists and other scientists use computer models to forecast solar storms and other solar activity.
- Storm arrival timing and pace can be predicted using current models. The storm’s structure or orientation, on the other hand, cannot be predicted.
- The magnetosphere can respond more intensely to specific magnetic field directions, resulting in more violent magnetic storms. As a result, improved space weather forecasts and more efficient techniques to secure satellites are required as the world’s reliance on satellites for practically every activity grows.
Conclusion- Geomagnetic Storm
Because of our increasing dependency on technical devices that can be impacted by electric currents and energetic particles high in the Earth’s magnetosphere, geomagnetic storms are more disruptive now than in the past. Therefore, more studies are required to assist us in preparing for and decreasing their effect. This essay covers everything you need to know about the Geo Magnetic Storm. It’s one of the most important topics you must know for the IAS exam. As a result, read the entire article about the Geomagnetic Storm. We’ve also discussed what causes a geomagnetic storm (also known as a solar storm), its effects, how to predict a space storm, and other information. In addition, one can go to the UPSC’s official website to learn more about the IAS test and further details. To learn more, go here.
FAQ- Geomagnetic Storm
It’s causing havoc with your internal clock. Headaches, palpitations, mood swings, and a general sense of being unwell can all be caused by a solar flare. As a result, Your thoughts are jumbled and chaotic, and you may exhibit more erratic behavior.
The Sun’s flares generate an aurora, which is a beautiful light show in the sky. Auroras are created when particles from the Sun collide with gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in spectacular light displays in the sky. Auroras can be observed frequently around the North and South Poles. On the North Pole, it’s known as the aurora borealis, or northern lights, while on the South Pole, it’s known as the aurora australis or southern lights. Because of the spectacular light show in the sky, auroras are a wonderful delight. Some of the energy and small particles from a solar storm can go down the magnetic field lines at the north & south poles into Earth’s atmosphere.
Sunspots are places on the Sun where the magnetic field is around 2,500 times stronger than Earth’s and much greater than anywhere else. The magnetic pressure rises due to the high magnetic field, while the surrounding atmospheric pressure falls. Sunspots are black regions that appear on the Sun’s surface. Because they are cooler than other portions of the Sun’s surface, they seem dark. However, a sunspot’s temperature is still extremely hot —around 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit!
Editor’s Note | Geomagnetic Storm
In summary, the above article informs you about Geo Magnetic Storm. We’ve also covered what causes a geomagnetic storm (also known as a space storm), its impacts, how to anticipate one, and other topics. Read this material thoroughly and make notes of all the key points. To pass the IAS test, one must first learn the exam syllabus and paper format. After that, you are welcome to browse our website. We’ve covered all the relevant information to know about the IAS exam. Exam format, syllabus, books, advice, and other details should all be known. Finally, best wishes!