There are many concepts one must cover for the IAS exam. So, we cover details of all the essential topics that will help you with the IAS exam preparations. This article covered all information related to the Biogeochemical Cycles in this article. Know about the Biogeochemical Cycles diagram, notes, and how to define Biogeochemical Cycles. It is one of the vital concepts for the IAS exam.
Introduction
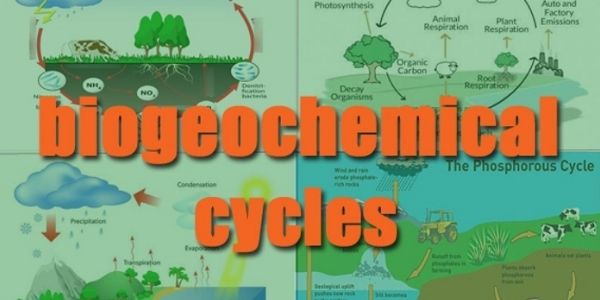
To begin with, bio means biosphere, geo means the geological components, and “chemical” means the elements that move through a cycle. Further, it is the pathway by which a chemical substance cycle the biotic and the abiotic compartments of Earth. The biotic compartment is the biosphere, and the abiotic compartments are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere.
The primary elements present in the energy from the sun, which is radiated back as heat, rest all other features are present in a closed system.
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
Below we have added all information on the Biogeochemical Cycles diagram and how to define the Biogeochemical Cycle. It is essential for one to make essential points while reading the article and study the same during the exam.
Biogeochemical Cycles Notes
- In the first place, Energy flows directionally through ecosystems, entering as sunlight and leaving as heat during the many transfers between trophic levels
- The biogeochemical is a contraction that refers to the consideration of the biological, geological, and chemical aspects of each cycle.
- Further, biogeochemical cycles flow in different forms from the nonliving components of the biosphere to the living components and back.
- Each biogeochemical cycle can be defined as having a reservoir pool, a larger and an exchange pool concerned with the rapid exchange between the biotic and abiotic aspects of an ecosystem.
Biogeochemical Cycles
- Gaseous Cycles – includes the Nitrogen, Carbon, Oxygen and Water Cycle.
- Further, Gaseous cycles tend to move more rapidly to adjust to changes in the biosphere because of the large atmospheric reservoir.
- They are perfect nutrients.
- Sedimentary Cycles – includes the Rock, Phosphorus and Sulphur cycle.
- This cycle vary from ne element to another, but each cycle consists fundamentally of a solution.
- These are imperfect as some nutrients lost get locked into sediments and are unavailable for immediate cycling.
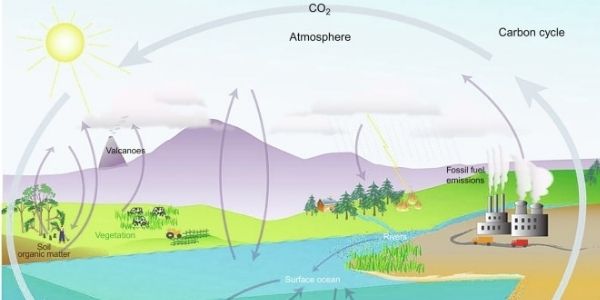
Carbon Cycle
Further, Carbon s one of the most vital elements for the happening of all cycles on earth. It is present in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Besides, you can see it as the most expensive substance diamond. It’s located in proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids, vitamins, and minerals. As we all know, all green plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight for photosynthesis. Carbon is thus present in the plant. Further, the green plants, when dead, are buried into the soil that gets converted into fossil fuels made from carbon.
Also, carbon is mainly produced when present in the form of fossil fuels (coal & oil). Further, it can be extracted for various commercial and non-commercial purposes.
Continued
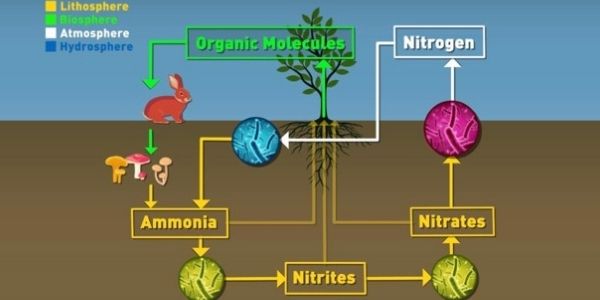
Nitrogen Cycle
Further, it is a biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into several forms, and it gets circulated through the atmosphere and various ecosystems such as terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Besides, our atmosphere includes around 78% of nitrogen, and nitrogen is present in proteins and essential nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. Further, you can find it in alkaloids and urea. Then, the nitrogen-fixing bacteria is located in the roots of legumes in part called root nodules. Additionally, the bacteria present in the origins of the plants convert this nitrogen gas into a usable compound called ammonia, and ammonia is supplied to plants in the form of fertilizers.
Amino acids are essential to make proteins. Further, animals consume proteins (animals eat plants that contain proteins). Besides, these animals die, bacteria in the soil convert nitrogen compounds back into nitrates and nitrites. Nitrogen passes from elemental in the atmosphere into nitrates and nitrites in soil and water.
Oxygen Cycle
Further, oxygen is one of the essential elements. 21% of the earth’s atmosphere consists of oxygen. Besides, you will find oxides of metals, silicon, carbonate, sulfate, nitrate, and other minerals in the earth’s crust. Humans and other animals inhale the oxygen exhale carbon dioxide, which the plants again take up.
Biogeochemical Cycles Types
Water Cycle
Further, water evaporates from the water bodies, and the condensation of this water vapour leads to rain. Then, the biogeochemical cycle is responsible for maintaining weather conditions. The process in which water evaporates and falls on the land as rain and later gets back to see through rivers is called a Water-cycle. Besides, a small amount of water goes down into the soil and becomes part of the underground water. Water flows through or over rocks that contain soluble minerals.
Phosphorous Cycle
Concerning the Phosphorous Cycle, phosphorous moves through the hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. Besides, it is extracted by the weathering of rocks. Due to rains and erosion, phosphorus is washed away in the soil and water bodies.
Sulphur Cycle
Lastly, the biogeochemical cycle moves through the rocks, water bodies, and living systems. Then, the sulfur is released into the atmosphere by rocks’ weathering and converted into sulfates. Further, these sulfates are taken up by the microorganisms and plants and converted into organic forms. Finally, animals consume it through food and when these animals are decomposed.
Importance of Biogeochemical Cycles
- In the first place, all these cycles through the ecosystem and move all vital elements for life to sustain.
- Further, these are important elements through the physical facets.
- These all cycles depict the association between living and non-living things in the ecosystems and enable the continuous survival of ecosystems.
- Besides, it is essential to comprehend these cycles to learn their effect on living entities.
- Later, some activities of humans disturb a few of these natural cycles and thereby affecting related ecosystems.

UPSC Exam
UPSC conducts the IAS exam every year, and we see lakhs of students applying for the exam. Further, get all vital information related to the IAS exam here. Know More. Additionally, it is also vital for one to go through the official website to help you with the latest exam information. It is essential to know about the exam procedure before applying for the exam. Besides, one needs to go through the previous year’s question papers and give mock tests. You can click on the links for more information on the same. Then, to get the best results in the exam, one must also follow some tips and read the success story of other IAS officers. Also, one must be careful while selecting the optional subjects. This specific article will help you with the Biogeochemical Cycle diagram and how to define Biogeochemical Cycles.
Further, read more here for the latest UPSC and the IAS exam information. Also, understand all detail before applying for the exam.
Conclusion – Biogeochemical Cycles
In this article, you will find all information related to the Biogeochemical Cycles diagram, notes, and other essential points that are important for the UPSC exam. We have covered various cycles like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen cycle, etc. It will help you with the IAS exam preparations. Also, get all information related to the other UPSC exam study materials vital for the IAS exam. Read More. It is essential for one to maintain a separate notebook where you will write down all essential points, and you can study the same during the exam. Further, we all know about the UPSC exam, and there are three main rounds. One must clear all three stages of the exam to become an IAS officer. We wish you good luck with the IAS exam, prepare well.
FAQs – Biogeochemical Cycles
Water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles.
Five types of cycles are the carbon cycle, Carbon cycle, SLH, and the carbon cycle.
The water cycle, Over two-thirds of the Earth’s surface, is roofed by water
Preparing for the IAS exam is a long process. First, one must know the IAS exam syllabus and the pattern of the paper. Further, it is essential for one to go through the official site.
Editor’s Note | Biogeochemical Cycles
In the above article, we have added all information related to the Biogeochemical Cycles and how to define Biogeochemical Cycles. Also, know about the Biogeochemical Cycle notes and diagram. As we have mentioned before, it is also one of the vital concepts for the UPSC exam. Further, to clear the IAS exam, one must work hard and put in all efforts. As we all know aware about the UPSC exam, is one of the popular and the toughest exams in India. Besides, there are many wishes to become the next IAS officer, but only with your hard work can one achieve it. But, it is not like any other exam. It only depends on you and how you will make it happen. Only your hard work and focus will help you get the best results in the exam.






