The Indus Valley Civilization represents the beginning of Indian history. Therefore, the topic of ‘Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) is crucial for the IAS Exam For both Prelims (Ancient History) and Mains (GS-I & Optional.) Therefore Don’t forget to read this article. In this article, we will discuss the introduction to the Harappan Civilization, the map of the Harappan Civilization, the decline of the Harappan Civilization (Indus Valley Civilization), Harappa, and Mohenjo Daro.
Introduction to Harappan Civilization
The Harappan culture, commonly known as the Indus valley civilization, flourished in the Indus Valley was the Indian subcontinent’s first known urban culture. The IVC was South Asia’s first significant Civilization, spanning a wide region of land in modern-day India and Pakistan (around 12 lakh sq. km). It flourished around 2,500 BC in western South Asia. The Civilization was discovered in 1921 in Harappa, Punjab, and subsequently in 1922 in Mohenjo Daro along the Indus River in Sindh (Sind). Both locations are in modern-day Pakistan, in the provinces of Punjab and Sindh, respectively. The Indus valley civilization is well-known for two enormous cities, Harappa and Mohenjo Daro, as well as more than 100 towns and villages, many of which were tiny in size. In 1980, the Mohenjo Daro ruins were designated a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Don’t forget to check out The Best History Books for UPSC – Ancient & Modern.
The largest of the four current urban civilizations in the Indus Valley Civilization are Mesopotamian or Sumerian Civilization, Egyptian Civilization, and Chinese Civilization.
Egyptian Civilization thrived on the banks of the Nile River, Mesopotamian Civilization flourished on the banks of the Tigris or Euphrates Rivers, and Chinese Civilization flourished on the banks of the Hwang Ho River, and IVC flourished on the banks of the Indus.
It is also called as the Bronze Age Civilization because it comes from the Bronze/Chalcolithic era. This concludes the Harappan Civilization Introduction.

Important Sites of Indus Valley Civilization
We will see the important Harappan civilization sites on a map and get a brief overview of these important IVC sites. In the Indus Valley civilization, there are seven important cities.
- Harappa
- Mohanjodaro
- Kalibangan
- Chanhudaru
- Dholavira
- Banawali
- Lothal
Here we provide a list of key sites in the Harappan civilizations (Indus Valley Civilization) with an introduction & map, and major discoveries which will be highly relevant for the UPSC IAS Prelims test.
List of Key Sites in the Indus Valley Civilization
| Site | Map | Excavated by | Important Findings |
| Harappa | Sahiwal District, Punjab, on the Ravi River’s banks | Daya Ram Sahni | – Cubical Limestone Weight Faience Slag Pottery with Indus Script – Human anatomy sandstone statues – Bullock cart made of copper – Granaries – Burials in coffins (Only founded in Harrapa) – Figurines made of terracotta |
| Mohanjo daro | Sind’s Larkana District on the Indus River | Banerjee | – Seals of the Unicorn (Most numbers of it in here) – Bronze statue of a dancing girl – Steatite statue of a guy with a beard – Buffalo in bronze – Great bath – A man’s seal with deer, elephants, tigers, and rhinos |
| Kalibangan | Rajasthan’s Hanumangarh District, on the banks of the Ghaggar River | Amlanand Ghose | – Lower fortified settlement – Drainage made of wood – Camel’s bones – cultivated land – Earthquake evidence – Camel’s bone and a wooden plough |
| Chanhudaru | Mullan Sandha, Sind, on the Indus River | N G Majumdar | – Shop for Bangle Factory – InkPot – Bead Makers shop – A dog’s footprint chasing a cat – Cart with a seated drive |
| Dholavira | Gujarat in the Kutchchh Rann | R S Bisht | – Water management that is exclusive – Massive reservoir of water – Dams, embankments, stadiums, and rock cut architecture are all unique water-harvesting systems. |
| Banawali | Haryana’s Fatehabad district | R S Bisht | – Barley Beads Oval Shaped Settlement – The only city in the world with radial streets – Plough toy – The greatest quantity of barley grains |
| Lothal | Gujarat, near the Gulf of Cambay, on the Bhogva River | R Rao | – Port Town Cemetery – Ivory weight distribution – Rice husk – Fire changes things. – Chess-playing – Copper dog – First manmade port |
This is a list of important Indus Valley civilization sites.
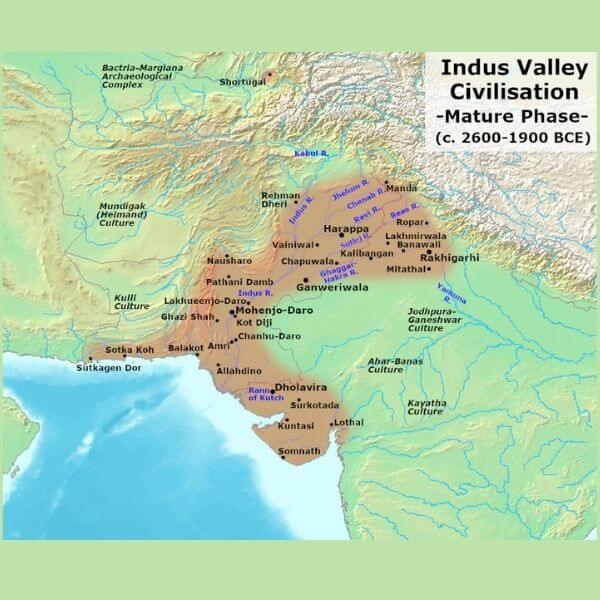
Now let us discuss the phases of Indus Valley Civilization and decline of Harappan civilization.
Phases of Indus Valley Civilization
After learning about the Stone and Copper Ages, it’s time to learn about the Bronze Age Civilization. The Civilization of the Indus Valley (IVC) .i.e. The IVC, Indus valley civilization, had three phases:
- The Early Harappan Phase (3300 to 2600 BCE),
- The Mature Harappan Phase (2600 to 1900 BCE), and
- The Late Harappan Phase (1900–1300 BCE)
Kot Diji represents the period preceding the Mature Harappan Phase. The Indus Valley Civilization had reached a mature stage by 2600 BC.
Early Harappan villages that matured into great urban centers include Harappa and Mohenjodaro in Pakistan and Lothal in India.
The Indus River Valley Civilization’s steady fall is said to have begun approximately 1800 BC, with most of the towns abandoned by 1700 BC. Later cultures, on the other hand, can see various characteristics of the Ancient Indus Valley Civilization.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the Late Harappan culture lasted until 1000-900 BC.

Decline of Harappan Civilization
- Around 1800 BCE, the decline of the Harappan Civilization began and eventually perished. The exact reasons for its death are still being disputed.
- According to one theory, the Indo-European group known as the Aryans invaded and conquered the Indus valley civilization.
- Various features of the Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) have been uncovered in later cultures, implying that Civilization did not vanish abruptly as a result of an invasion.
- However, many academics believe that natural forces are to blame for the Decline of Harappan Civilization. Natural variables such as geological and climatic conditions.
- The Indus Valley region is thought to have suffered tectonic disturbances that resulted in earthquakes. Rivers’ courses were also altered or dried up as a result of this.
- A change in rainfall patterns could be another natural factor.
- There could possibly have been significant changes in river courses, resulting in floods in food-producing areas.

Important facts on Indus Valley
- The term “Indus Valley Civilization” was coined by John Marshall, who was the first to use it.
- According to radiocarbon dating, the IVC existed between 2500 and 1750 BC.
- Mohenjodaro and Harappa are the two capital cities.
- Sutkagendor, Balakot, Lothal, Allahdino, and Kuntasi are the harbor cities.
- Many items and art forms were created by the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- The Indus Valley Civilization had a population of over 5 million people.
- They had state-of-the-art sanitation systems.
- Before any other ancient civilization, the people of the IVC understood about and practiced water channeling and wastewater disposal.
- Archaeologists have discovered no resemblance to a temple, palace, or monument.
- Historians aren’t sure what caused the IVC demise.
Conclusion- Indus Valley Civilization
For the UPSC Civil Services Examination, this is a quick summary of the Indus Valley Civilization & Harappan Civilization Map. In our General Studies-I course for the UPSC Mains test, we go over this topic in depth. The introduction to the Harappan Civilization, the Harappan civilization map, the demise of the Harappan Civilization and the Harappa and Mohenjo Daro have all been described here. It will assist you in preparing for the IAS test. In addition, one must review past year’s question papers and take practice examinations. For the most up-to-date UPSC and IAS exam information, click here.
FAQ
The Indus Valley Civilization was originally discovered in 1921 in the Punjab region of Harappa, and then in 1922 in the Sindh (Sind) district of Mohenjo-Daro, near the Indus River.
The name Mohenjo Daro is thought to mean “the dead mound.” The site’s archaeological significance was initially acknowledged in 1922, one year after Harappa was discovered. Following investigations, it was discovered that the mounds contain the ruins of the Indus civilization’s biggest city.
Rai Bahadur Daya Ram Sahni began the first significant excavations at Harappa in 1920. His study, as well as contemporaneous excavations at Mohenjo Daro, were the first to reveal the presence of the forgotten Indus Valley civilization as the Indian subcontinent’s earliest urban culture.
Aryan civilization was based on religion. Hinduism was founded on the fusion of Aryan religious beliefs with the habits of those already living in the valley. The Aryans sacrificed to a variety of gods in order to adore them. They performed numerous complicated ceremonies and took great care to maintain ceremonial purity in accordance with their varna.
Editor’s Note | Supreme Court of India
In conclusion, the IAS test is one of India’s most essential and difficult examinations. Furthermore, the exam attracts a large number of students and working professionals. This article will learn about the Supreme Court of India (Delhi) – Total Judges, Established and Post. A link to the official website has also been supplied. Furthermore, the exam requires a lot of time. Therefore, one must establish a proper strategy and provide time for all of the exam’s subjects and time for review. Aside from the material and topics, current affairs play a significant role in the IAS prelims and mains examinations. The current advancements in various domains of the world are used to frame objective and subjective questions. We wish you the best of luck.







