UPSC conducts exam for three All India Services. First is the Indian Administrative Services or IAS. Second is the IPS. The full form of IPS is the Indian Police Service. Next is the Indian Forest Services. Remember, Indian Foreign Services is not an All India Service. IPS Officer is a respected and honored profession in India. Therefore, many aspirants aim for this position. UPSC conducts exams for the IAS. Similarly, IPS can be a desired service for candidates. Hence, this is the second most popular service. IPS salary is an attractive avenue. The IPS exam is further discussed in this article. Furthermore, we shall discuss the Indian Police Ranks.

IPS Exam
To begin with, let us first talk about the IPS exam. UPSC conducts the civil service exam. The same exam selects IPS Officer and IAS Officer. It selects a few other services as well. Hence, the allotment of services depends upon various factors. Firstly, you are expected to fill a detailed form. The form contains an order of choice. Choose your preferences according to your priority. After you fill in the preferences, UPSC considers your rank. Rank determines your service as well. Vacancies influence recruitment. Therefore, being an IPS officer is not that easy. But, don’t worry it isn’t impossible either.
Meanwhile, let’s discuss the IPS exam. There is no such different exam for IPS Officer. Therefore, the civil service exam is the key to this service as well. The IPS exam contains three stages. Candidates need to first qualify for the prelims test. Then, candidates must attempt CSE Mains. Hence, candidates need to pass the prelims exam. You must clear the Mains exam. Afterward, you shall be called for an interview. The UPSC panel conducts the interview.
IPS Exam Syllabus
To check the syllabus: Click here. GS Paper I is an integral part of prelims. Paper-II is an aptitude test. Also called as Civil Services Aptitude Test. The acronym is CSAT. Candidates must score in GS Paper I as per merit. This is the first step to become an IPS Officer. Whereas, GS paper II is a qualifying paper. Therefore, a CSAT paper needs only a 33% score. Accordingly, aspirants appear for the mains exam. Prelim is an objective type test. Whereas, Mains is subjective in nature. Prelims follow the negative marking system. However, there is no negative marking in the mains. To check previous years’ question papers: Click here. Hence, it is advisable to analyze these papers while preparation.
The mains exam comprises of the following:
- Paper A
- Paper B
- GS Paper I
- GS Paper II
- General Studies Paper III
- General Studies Paper IV
- Optional Subject: Paper I
- Optional Subject: Paper-II
About the Papers
Paper A and B are language papers. These papers are qualifying in nature. However, candidates must score a minimum of 25%. A score below 25% leads to the non-calculation of other papers. Passing in all papers is important to be an IPS Officer.
- Now, let’s talk about the GS paper I. GS Paper, I contain Indian Culture. It consists of History. Next, it contains Geography. Lastly, it contains the Indian Society.
- GS Paper II consists of Polity. It also contains Governance. A brief knowledge of the Indian Constitution is necessary. Therefore, you must prepare well.
- GS Paper III contains the Indian Economy. It also contains Science and Tech. Next is the environment. This paper contains Disaster Management as well. Lastly, comes Internal Security. Therefore, there are 5 primary topics.
- GS Paper IV consists of Ethics. It is the most important paper. Therefore, it requires good preparation.
- The optional paper has two phases. You must choose an Optional Subject. UPSC provides a list of Optional subjects. You can select any one of them. The syllabus differs as per the subject chosen.

IPS Officer: Eligibility and Full Form
Furthermore, we discuss the criteria to become an IPS Officer. Firstly, candidates must clear the IPS Exam. The IPS Full Form is Indian Police Services. Now let’s talk about eligibility.
Firstly, let’s discuss the adequacy to appear for the IPS Exam:
One can appear for exam, only if he’s eligible. Therefore, check your eligibility here.
- Must be a citizen of India.
- Must complete 21 years. (On 1st Aug of exam year).
- Must hold a degree from a recognized university.
Eligibility w.r.t age and attempts
AGE WISE
- General Category: 32 years of age.
- OBC: 35 years of age.
- SC/ST: 37 years of age.
- Handicapped General Category: 42 years of age.
- Handicapped OBC Category: 45 years of age.
- SC/ST Category Handicapped: 47 years of age.
ATTEMPT WISE
- General Category: 6 attempts.
- OBC: 9 attempts.
- SC/ST: unlimited attempts.
- Handicapped (General and OBC): 9 attempts.
- Handicapped ( SC/ST): Unlimited attempts.
Physical Eligibility for IPS Officer
| Category | Male | Female |
| Eye Sight | Good eye distant vision: 6/6 or 6/9 | For worst eye: 6/12 or 6/9. J1 Near vision for Good eye. J2 for Worst eye. |
| Height | 165 cm. For ST- 160 cm | 150 cm. For ST- 145 cm. |
| Chest | Min 84 cm. Expansion 5 cm. | Min 79 cm. Expansion 5 cm. |

Training for IPS
Like every other service, an IPS Officer undergoes training. However, the training for IPS is quite distinct. The training is given in four parts. Let us look at them.
- Foundation Course: Firstly, the probationers undergo a foundational course. The duration of this course is 3 months. This course is common for other services. Therefore, it takes place at LBSNAA, Mussoorie. It is also called the basic course.
- Phase I: Phase one training is a basic course. The course duration is 11 months. This training takes place at SVPNPA. That is Sardar Vallabhai Patel National Police Academy. This academy is in Hyderabad. Hence, the probationers have now imparted training at Hyderabad.
- Practical Training: Next we shall talk about Practical training. This training takes place in a district. The district of practice varies from cadre to cadre. As a result, candidates get some practical knowledge here. This training lasts for 6 months.
- Phase II: Lastly, let us discuss the Phase II training. Phase II training duration is One month. This is the shortest course of all. This training takes place at SVPNPA.
Objective of the training
Every civil service undergoes training. Likewise, IPS also train their officers. (IPS Full Form: Indian Police Service). However, it is important to understand the objectives of training. To begin with, the training imparts overall physical training. It also gives emotional and ethical knowledge. It helps an IPS Officer understand his/her roles and duties. The introduction of the basic structure takes place during the foundation. The first phase introduces the respective service. Whereas the foundational course is generic, this phase is specific. Therefore, it gives an insight into your actual role and duty. In addition to this, aspirants undergo practical training. Accordingly, aspirants reach the next level of training. Phase II is the last course. This course marks the completion of the training period.
Basic Course Subjects for an IPS Officer
The basic course includes a few compulsory indoor subjects. It also includes some optional subjects. One section of the course is theory. Whereas, the other section includes physical training.
Let us note down the theory subjects first. Then we shall move towards the next section.
- Indian Evidence Act, 1872.
- Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973.
- Indian Penal Code, 1860.
- Police in Modern India.
- Special Laws.
- Investigation.
- Prevention of crime and criminology.
- Forensic Science.
- Forensic Medicine.
- Internal Security.
- Maintenance of Public peace and order.
- Police leadership and management.
- Ethics and Human rights.
- Information and Technology.

Next, let us look at the physical training subjects.
- Yoga
- Physical Fitness.
- Swimming.
- Drill.
- Unarmed Combat.
- Tactics and fieldcraft, map reading.
- First Aid and Ambulance Drill.
- Equitation (Horse Riding)
IPS Training Optional Subjects
IPS Training includes both compulsory and optional subjects. Therefore, candidates need to select an optional subject. Meanwhile, let us look at the list of Optional Subjects.
- Motor mechanism and Driving.
- Hindi
- Regional Language.
- Police telecoms and Control room Operations.
Indian Police Ranks and IPS Salary
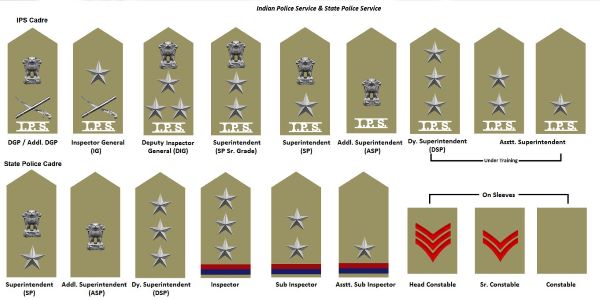
We’ve already discussed the eligibility for IPS Exam. We have also talked about training. Now, let us discuss the Indian Police Ranks in detail. Indian Police Ranks are fixed by the government. The IPS Salary differs from Rank to Rank. The IPS Salary is flexible in nature. An IPS Officer enjoys other perks as well. Let us start by discussing the topmost rank. The first on the list is the Director-General of Police. Simply, DGP or The Commissioner of Police. Accordingly, the next in rank is the Additional director-general. It is also designated as Special Commissioner of Police. After this rank comes the Inspector General of Police. Also known as the Joint Commissioner of Police.
Further, there is a DGP. The state designates it as an additional commissioner of police. Therefore, a rank may have two designations. This is because IPS is an all India service. Next, Indian Police Rank is Sr. Superintendent of Police. Hereby, he’s also designated as DCP. After that comes the ASP. Also known as Additional DCP. Subsequently comes the DSP. Also, designated as Assistant Commissioner. That is, ACP. Therefore, this is the last in the Indian Police Ranks. Hence, there are 8 Indian Police Ranks. In addition to this, let us talk about the IPS Salary in the next salary.
IPS Salary
In addition to the salary, exam, and eligibility, let us discuss the IPS Salary. IPS Full Form is Indian Police Services. The IPS Salary is now as per the 7th Pay Commission recommendations. Therefore, we shall discuss the rank wise salary distribution. Note that the salary discussed here doesn’t include other perks. Moreover, IPS Officer receives allowances.
The DGP receives the highest salary in comparison to other ranks. Therefore, the salary reduces with a decline in rank. Hence, the DGP receives INR 2,25,000 as his salary. Next, the additional DGP enjoys a salary of INR 2,05,400. Next in rank is IG. Thereby, an IG receives INR 1,44,200. Consequently, the DIG enjoys a salary of INR 1,31,100. The Sr SP ranks 5th in position. Accordingly, he receives a salary of INR 78,800. After this comes the Additional SP. Being lower in rank he receives a salary of INR 67,700. Lastly, the Dy Superintendent receives a salary of INR 56,100. Note that an IPS Officer receives INR 56,100 at the start of his service. Ultimately, the salary upgrades from time to time.
FAQ Section | IPS Officer
No, you cannot appear for the exam unless your 21 years of age. Therefore, younger candidates cannot appear. However, you can start preparing before you turn 21 years.
Yes, both these services come under civil services. UPSC conducts exam for the All India Services. Therefore, services are allotted as per vacancy and preference.
Cadre allocation too is based on ranks and preferences. It also depends upon the vacancy. IPS cadres are grouped into five zones.
Editor’s Note | IPS Officer
In conclusion, we’d like to say that it takes a great effort to become an IPS Officer. Aspirants are not only expected to ace the written tests. But, they are also expected to maintain physical discipline. Consistency is the most important. An IPS Officer is expected to be responsible. These small behavioral changes will help you achieve your dream. One must learn to face new challenges every day. The method you use to deal with these problems will define your career. An IPS Officer is seen as a protector and guardian of the civilian population. Therefore, becoming an IPS Officer is reputable. It is important to realize your roles early. Therefore, you will stay motivated throughout your profession. Self-motivation works wonders in an aspirant’s life.