Current Account Deficit (CAD): Why It Matters for India’s Economic Stability
Introduction
The Current Account Deficit (CAD) is a key indicator of a country’s external sector health and macroeconomic stability. For an emerging economy like India, which is highly integrated with global trade and capital flows, managing CAD is crucial for maintaining currency stability, adequate foreign exchange reserves, and investor confidence. Persistent or widening CAD can expose the economy to external vulnerabilities, while a manageable deficit can support growth through capital inflows. For UPSC aspirants, CAD is an essential GS Paper III topic closely linked with Balance of Payments, exchange rate dynamics, and external sector management.
Understanding Balance of Payments (BoP)
What is Balance of Payments?
Balance of Payments is a systematic record of all economic transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world during a given period.
Major Components of BoP
- Current Account
- Capital Account
- Financial Account
- Errors and Omissions
What is the Current Account?
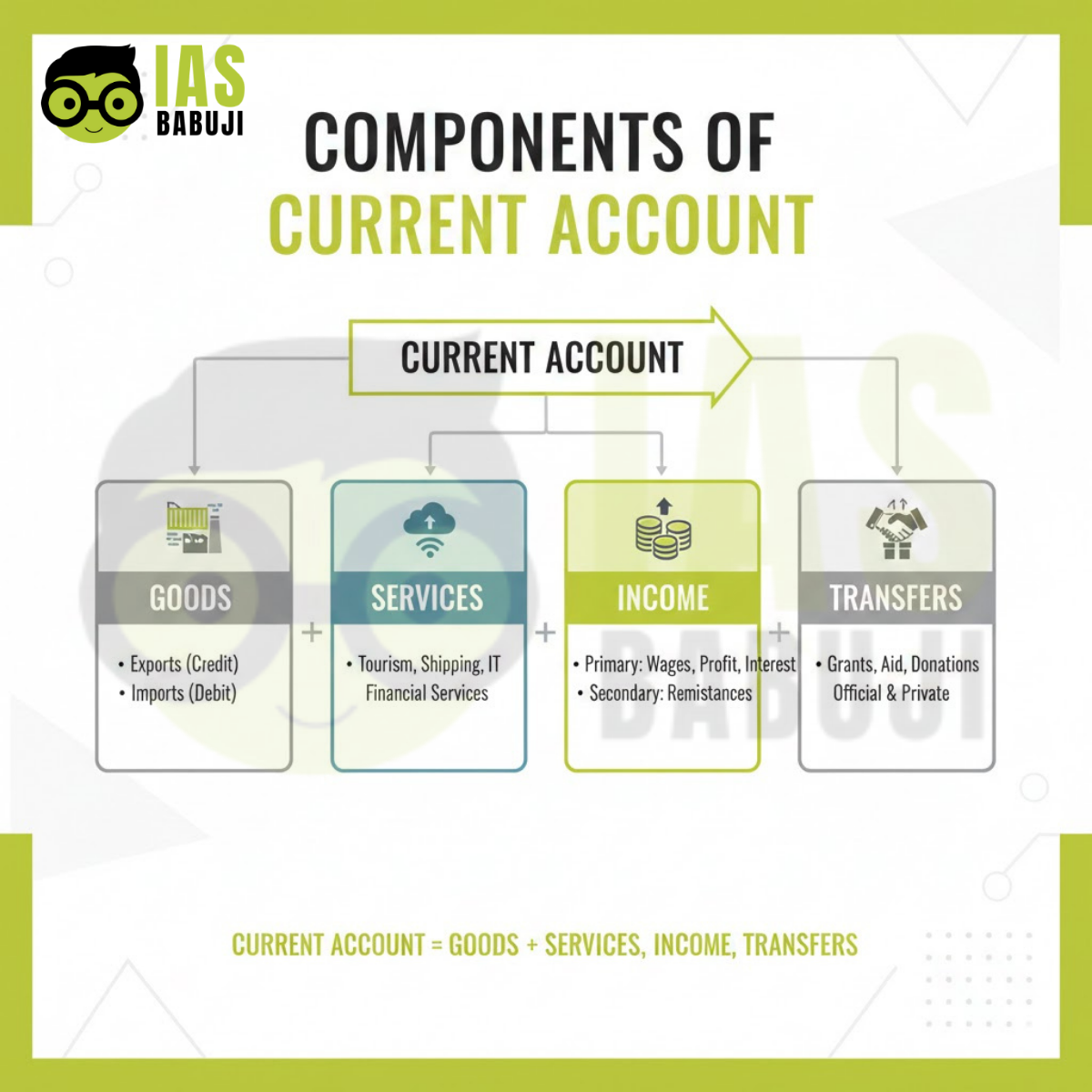
The current account records transactions related to:
- Trade in goods
- Trade in services
- Primary income (investment income)
- Secondary income (transfers such as remittances)
What is Current Account Deficit (CAD)?
A Current Account Deficit occurs when a country’s current account outflows exceed its inflows.
In simple terms, it means the country is importing more goods, services, and income than it is exporting.
Components of India’s Current Account
Trade Balance
- Export and import of goods
- India typically runs a merchandise trade deficit
Services Balance
- IT, software, and business services exports
- Often generates surplus for India
Primary Income
-
Interest and profit payments on foreign investments
Secondary Income
- Remittances from Indians working abroad
- Major stabilising factor for India
Causes of CAD in India
High Import Dependence
- Crude oil and petroleum products
- Electronics and capital goods
Global Commodity Price Volatility
-
Rise in oil and commodity prices increases import bill
Weak Export Performance
- Global slowdown
- Competitiveness issues
Exchange Rate Movements
-
Depreciation of rupee raises import costs
Domestic Demand Recovery
-
Higher imports during economic expansion
Why CAD Matters for India’s Economic Stability
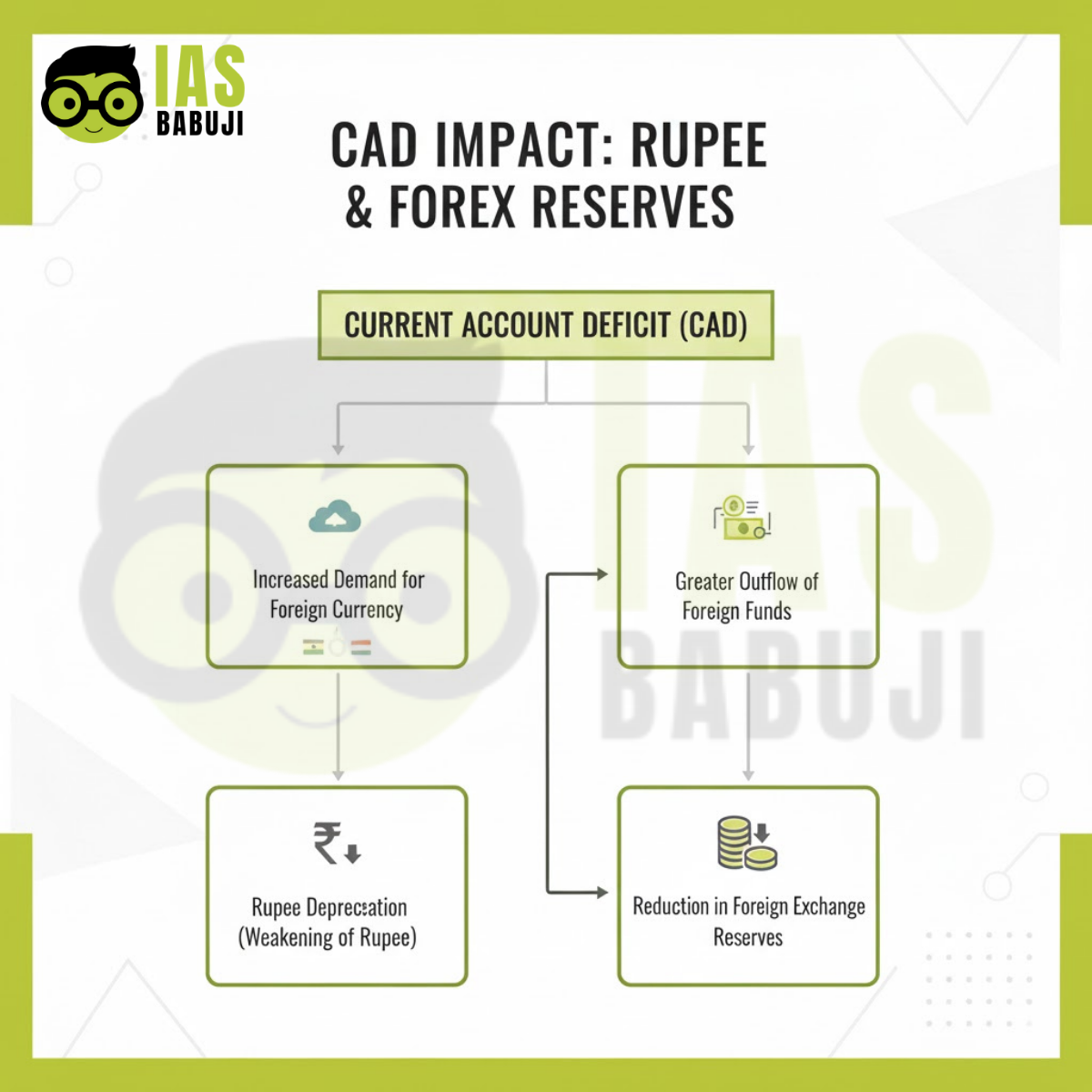
Impact on Rupee
- Higher CAD increases demand for foreign currency
- Leads to depreciation pressure on the rupee
Impact on Foreign Exchange Reserves
- RBI may use reserves to stabilise currency
- Sustained CAD can erode reserve buffers
Impact on Inflation
-
Rupee depreciation increases imported inflation
Impact on Investor Confidence
- High CAD signals external vulnerability
- May reduce capital inflows
CAD and Foreign Exchange Reserves
Foreign exchange reserves act as a cushion against external shocks.
- Adequate reserves help finance CAD
- Strengthen confidence in the economy
- Allow RBI to manage volatility in forex markets
India’s strategy focuses on maintaining sufficient reserves to cover imports and external liabilities.
Financing the Current Account Deficit
CAD is financed through:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
- External commercial borrowings
- NRI deposits
Stable capital inflows are critical for managing CAD sustainably.
Sustainable Level of CAD
- A CAD of around 2 to 2.5 percent of GDP is generally considered manageable for India
- Sustainability depends on the quality of capital inflows and global conditions
Role of RBI in Managing CAD
Exchange Rate Management
- Managed float regime
- Intervention to curb excessive volatility
Monetary Policy Measures
-
Interest rate adjustments to manage capital flows
Regulatory Measures
-
Liberalising or tightening capital flows when required
Policy Measures to Reduce CAD
- Export promotion and diversification
- Reducing import dependence through Make in India
- Boosting renewable energy to cut oil imports
- Enhancing services exports
- Encouraging stable capital inflows
Way Forward
- Strengthening manufacturing exports
- Improving trade logistics and competitiveness
- Maintaining adequate forex reserves
- Coordinated monetary and trade policy
A balanced approach is essential for long-term external sector stability.
Conclusion
The Current Account Deficit is a crucial indicator of India’s external economic health, reflecting the balance between domestic consumption and global integration. While a moderate CAD can support growth by attracting foreign capital, a persistently high deficit exposes the economy to currency volatility, inflationary pressures, and external shocks. India’s experience highlights the importance of strong services exports, remittances, and adequate foreign exchange reserves in managing CAD. Going forward, reducing import dependence, strengthening export competitiveness, and ensuring stable capital inflows will be key to maintaining external sector stability. For India, prudent management of CAD is not merely a macroeconomic necessity but a strategic requirement for sustainable and resilient economic growth.
FAQs
What is Current Account Deficit?
CAD occurs when a country’s current account outflows exceed inflows.
Is CAD always bad for the economy?
No, a moderate CAD can support growth if financed sustainably.
How does CAD affect the rupee?
Higher CAD increases depreciation pressure on the rupee.
Which UPSC paper covers CAD?
GS Paper III (Indian Economy).
SEO Meta Data
Meta Title:
Current Account Deficit (CAD) in India: Meaning and Economic Impact | UPSC GS III
Meta Description:
Detailed GS III analysis of Current Account Deficit in India covering BoP basics, rupee impact, forex reserves, and policy measures.
Tags (comma-separated)
Infographic Prompts with Placement
Infographic 1: Components of Current Account
Prompt:
“Clean infographic explaining components of current account including goods, services, income, and transfers, exam-oriented layout, color theme #b3c839”
Placement: After section “What is the Current Account?”
Infographic 2: CAD Impact on Rupee and Forex Reserves
Prompt:
“Flowchart infographic showing how CAD affects rupee value and foreign exchange reserves, simple arrows and icons, academic style, color #b3c839”
Placement: After section “Why CAD Matters for India’s Economic Stability”







