Border Infrastructure as a Strategic Asset: Lessons from India’s Northern Frontiers
Introduction
Border infrastructure has emerged as a decisive factor in modern national security. In India’s context, the experience of prolonged standoffs and tensions along the northern borders—particularly with China—has highlighted how roads, tunnels, bridges, and logistics networks are no longer merely developmental assets but strategic enablers. India’s northern frontiers, stretching across Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh, present difficult terrain, harsh climate, and logistical challenges. Strengthening border infrastructure in these regions has become central to India’s defence preparedness, deterrence capability, and territorial integrity.
Strategic Importance of Border Infrastructure
Border infrastructure determines the speed, scale, and sustainability of military mobilisation. In mountainous terrain, the ability to move troops, artillery, and supplies quickly can alter the balance during crises. Robust infrastructure also supports civilian development, reduces regional isolation, and strengthens India’s administrative presence in border areas.
From a strategic perspective, border infrastructure serves three critical purposes:
- Rapid deployment and logistical support for armed forces
- Deterrence by signalling preparedness and resolve
- Integration of border regions into the national economic and governance framework
India’s Northern Frontiers: A Challenging Geography
India’s northern borders are characterised by high altitude, extreme weather, and fragile ecosystems. Historically, difficult terrain and underdeveloped connectivity limited both civilian movement and military logistics. This infrastructure deficit placed India at a disadvantage, especially when compared to China’s extensive road, rail, and air connectivity on the Tibetan plateau.
The experience of border tensions has reinforced the lesson that terrain cannot be an excuse for strategic vulnerability. Instead, it must be addressed through engineering innovation and sustained investment.
Roads as Strategic Enablers
Road connectivity remains the backbone of border infrastructure. Over the last decade, India has accelerated the construction of all-weather roads along the northern borders under agencies such as the Border Roads Organisation (BRO).
Strategically significant roads enable:
- Faster troop mobilisation during emergencies
- Regular patrolling and surveillance
- Sustained supply chains in remote areas
Improved road networks reduce response time, enhance operational flexibility, and ensure that forces are not constrained by seasonal or weather-related disruptions.
Tunnels and Bridges: Overcoming Natural Barriers
Tunnels and bridges play a transformative role in high-altitude border regions. By bypassing avalanche-prone passes and fragile mountain routes, tunnels ensure year-round connectivity.
Strategic tunnels:
- Maintain all-weather access to forward areas
- Reduce logistical vulnerability during winters
- Enhance civilian mobility and economic activity
Similarly, modern bridges capable of bearing heavy military equipment allow seamless movement across rivers and valleys, directly strengthening operational readiness.
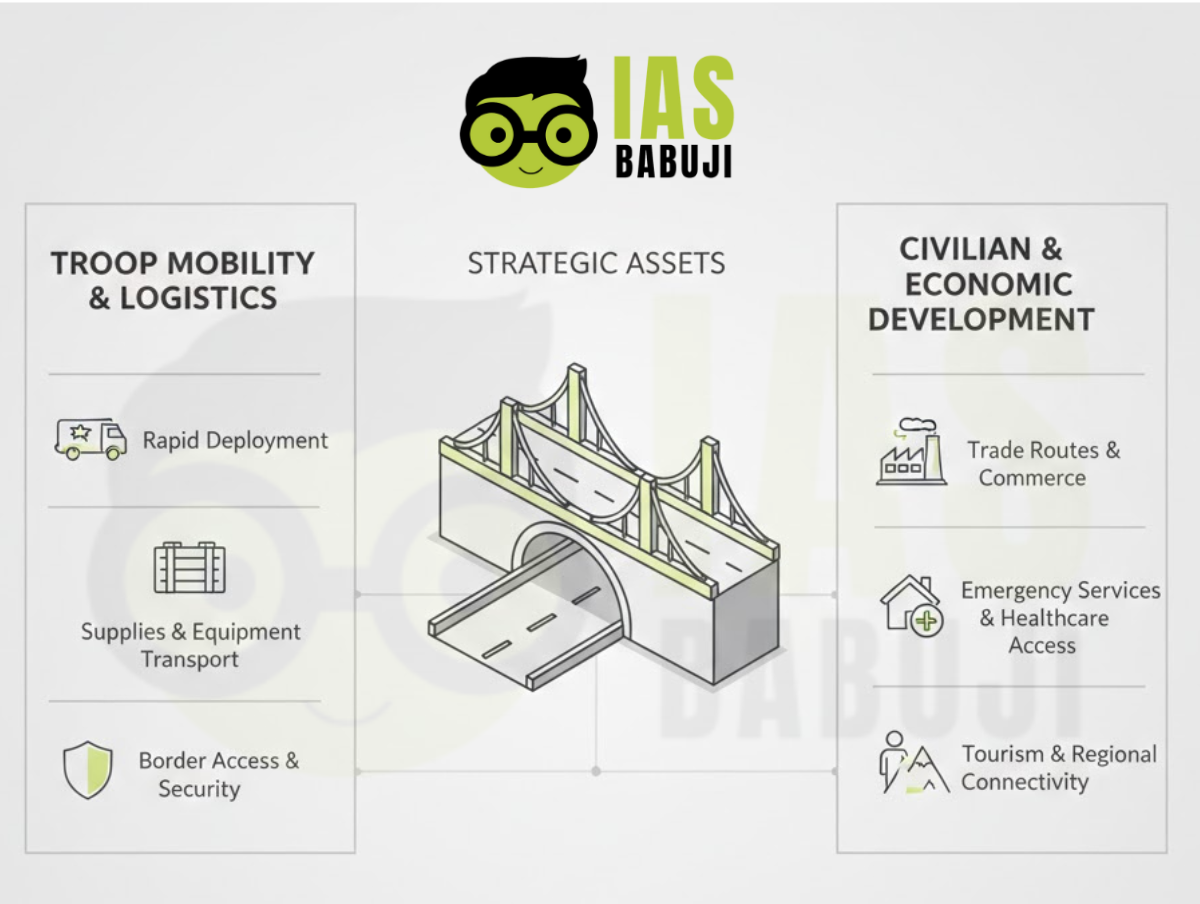
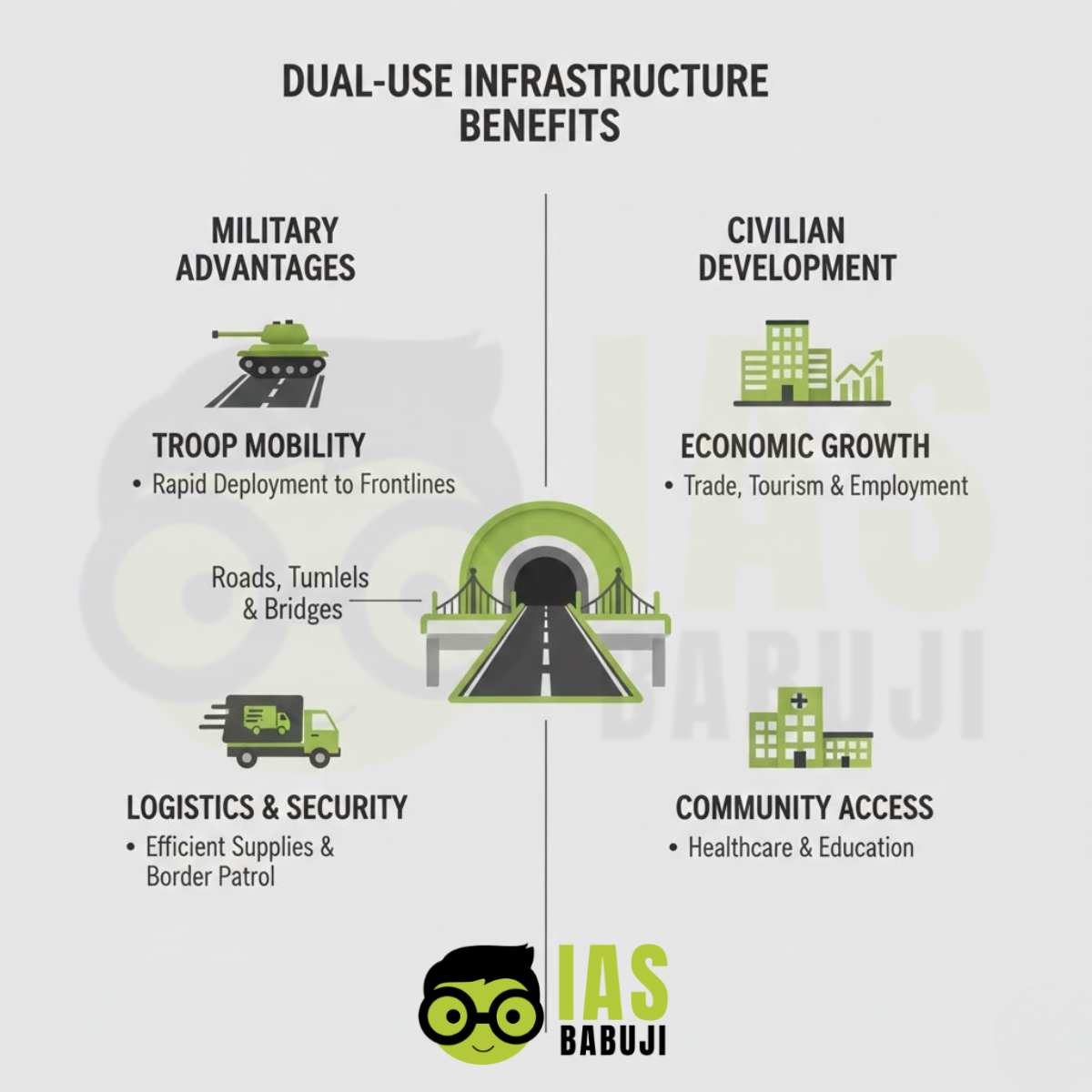
Dual-Use Infrastructure: Military and Civilian Synergy
A key lesson from India’s northern frontiers is the value of dual-use infrastructure. Roads, airstrips, communication networks, and logistics hubs serve both civilian development and military purposes.
Dual-use infrastructure:
- Supports local economies and tourism
- Improves access to health, education, and markets
- Enhances military logistics without creating exclusive defence zones
This approach aligns security objectives with inclusive development, reducing alienation in border regions.
Strategic Competition and the China Factor
China’s extensive border infrastructure development has altered the strategic landscape along the Line of Actual Control. High-quality roads, railways, and air bases on the Chinese side enable rapid force concentration.
India’s recent infrastructure push is a strategic response aimed at restoring balance and deterrence. Infrastructure development is thus not merely reactive but essential to prevent strategic asymmetry and ensure a credible defence posture.
Challenges in Border Infrastructure Development
Despite progress, several challenges persist.
Environmental concerns and fragile ecosystems require careful planning.
High costs and technical complexity delay project completion.
Coordination between civilian agencies, defence forces, and state governments remains a challenge.
Addressing these issues demands long-term planning, technological innovation, and institutional coordination.
Way Forward
India’s border infrastructure strategy must remain sustained and forward-looking.
- Prioritising critical corridors and strategic locations
- Integrating technology such as satellite monitoring and smart logistics
- Strengthening the institutional capacity of agencies like BRO
- Ensuring environmental sustainability alongside strategic needs
Such an approach will ensure that infrastructure remains a long-term strategic asset rather than a short-term response.
Conclusion
Border infrastructure has emerged as a cornerstone of India’s national security strategy. The lessons from India’s northern frontiers clearly demonstrate that roads, tunnels, bridges, and dual-use assets are not merely developmental projects but instruments of deterrence, resilience, and sovereignty. By transforming geography from a constraint into a strategic advantage, India can secure its borders, empower its frontier communities, and strengthen its overall defence posture. In an era of complex security challenges, robust border infrastructure is indispensable for both peace and preparedness.
FAQs
Why is border infrastructure important for national security?
It enables rapid troop deployment, sustained logistics, and effective deterrence in border regions.
What is dual-use infrastructure?
Infrastructure that supports both civilian development and military operations.
Which regions are India’s northern frontiers?
Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
How does China’s infrastructure affect India’s strategy?
China’s advanced connectivity necessitates India’s infrastructure push to maintain strategic balance.
Which UPSC paper covers border infrastructure?
Primarily GS Paper III, with links to GS Paper II and Essay.