Governor-General Acts Before 1857: Features & Chronology
GS Paper 1 – History (Pre-Independence India)
The Governor-General of India was the head of the British administration in India during the colonial period. Several Governor-General Acts passed before 1857 defined the powers, structure, and governance framework of the British administration. These acts are important for UPSC Prelims because questions are often factual, chronology-based, or elimination-oriented MCQs.
Understanding the features, year of enactment, and powers introduced helps aspirants eliminate incorrect options in MCQs effectively.
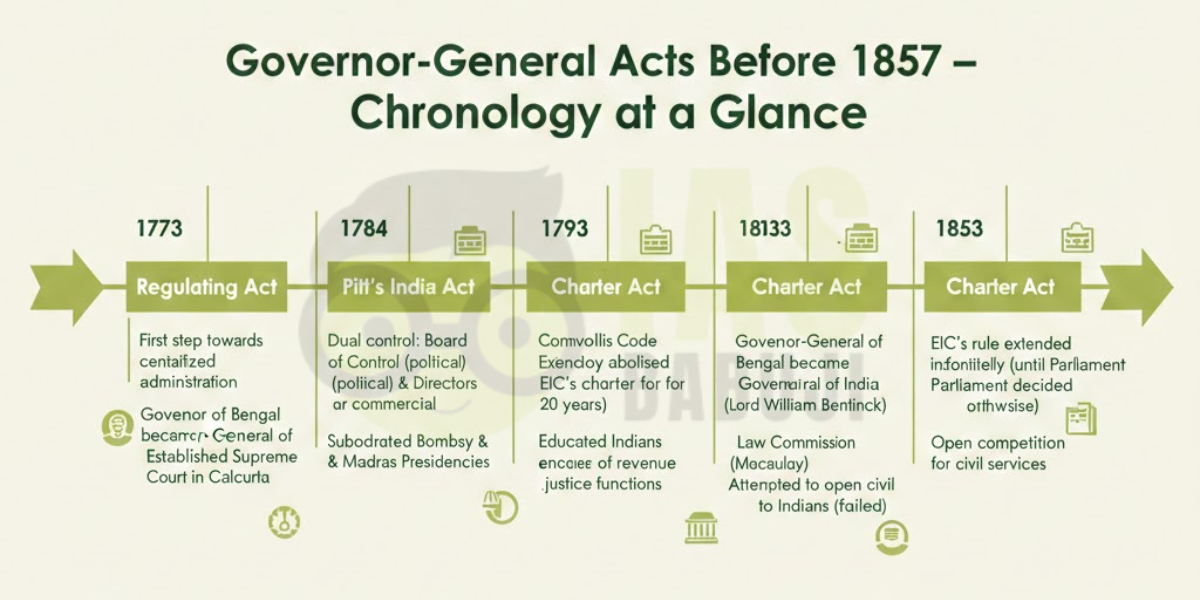
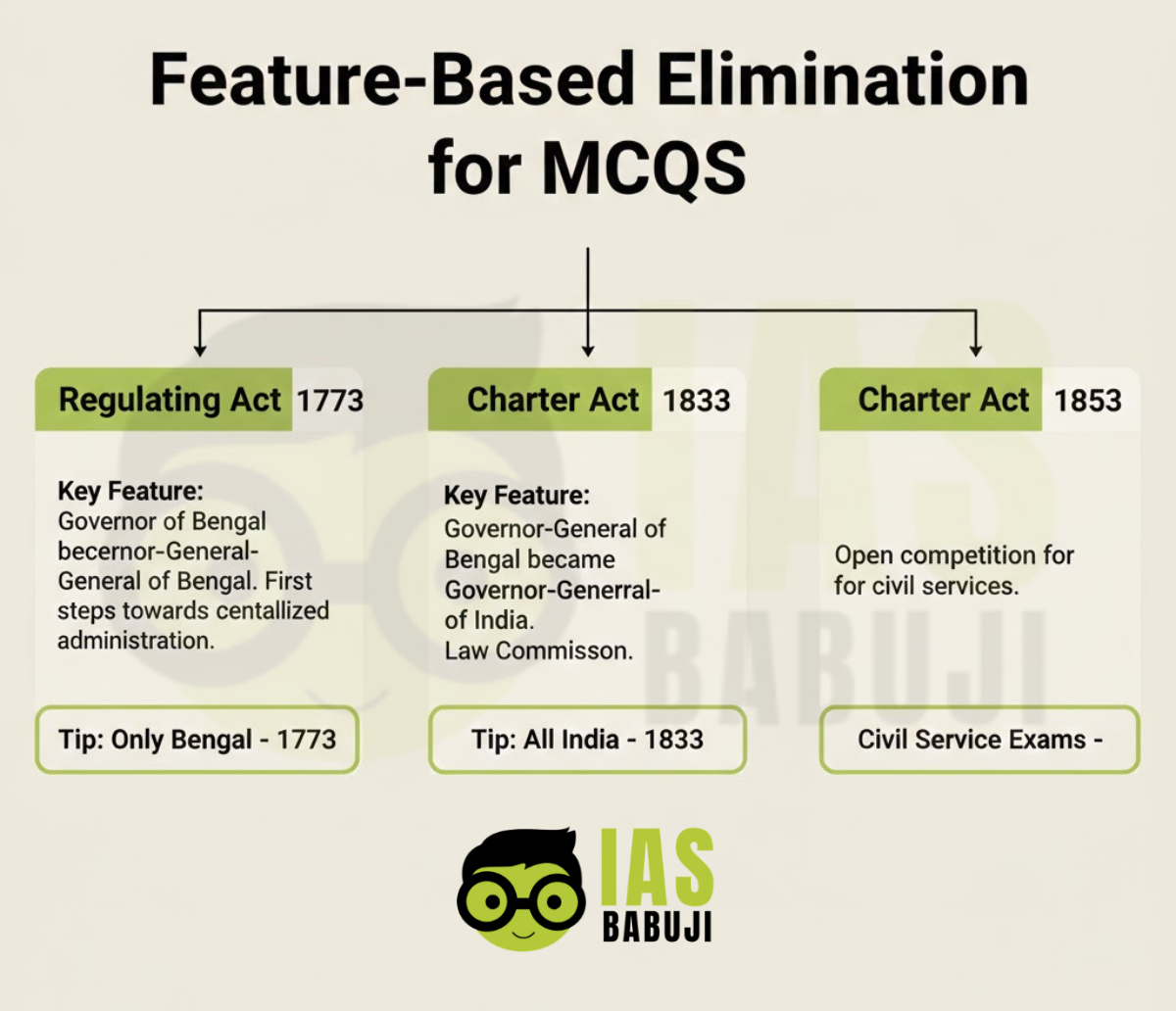
1. Regulating Act of 1773
Key Features:
- Introduced the office of the Governor-General of Bengal
- First attempt to regulate the East India Company by the British Parliament
- The Supreme Council of Bengal was created (4 members) to assist the Governor-General
- The Governor-General could override decisions of other governors in India
- The Chief Justice of the Supreme Court at Calcutta was established
Significance:
- Laid the foundation for British administrative control over India
- Limited parliamentary oversight was introduced
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- First Governor-General: Warren Hastings
- Only Bengal, not all India, initially
2. Pitt’s India Act of 1784 (Also called East India Company Act)
Key Features:
- Established dual control – Company retained commercial rights; British government retained political control
- The Board of Control was created in Britain to oversee political matters
- Governor-General of Bengal’s powers strengthened over other Presidencies (Madras & Bombay)
- Introduced the subordination of the Supreme Council to the Governor-General in legislative matters
Significance:
- Balance between British Parliament oversight and Company autonomy
- Strengthened the Governor-General’s executive authority
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- Also called Act of 1784 or Pitt’s India Act
- Introduced the system of dual control
3. Charter Act of 1793
Key Features:
- Extended the East India Company’s charter
- Strengthened the Governor-General’s legislative powers
- The Governor-General could issue regulations for all Presidencies
- No substantial change in the dual control system
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- Introduced renewed powers for the Governor-General in legislative matters
- Retained the Supreme Council system
4. Charter Act of 1813
Key Features:
- Renewed the Company’s charter
- Ended the company’s commercial monopoly in India, except for tea and trade with China
- Allowed the British government to intervene in education and religion in India
- The Governor-General could make regulations in all Indian territories
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- Important for education and missionary activity
- Marked early intervention in socio-cultural affairs
5. Charter Act of 1833 (Also called Government of India Act 1833)
Key Features:
- Made the Governor-General of Bengal the Governor-General of India (all India)
- Appointed a Law Member in the Council (legal advisory)
- Introduced centralization: The Governor-General now had legislative powers over all India
- Commercial powers of the Company ended
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- First all-India Governor-General
- Key in centralizing administration
6. Charter Act of 1853
Key Features:
- Introduced open competitive examinations for civil services in India
- Expanded legislative powers of the Governor-General
- Made the Council of the Governor-General larger and more representative
- Set up a framework for administrative and legal reforms
Factual Tip for MCQs:
- First merit-based civil service exams
- Preceded the 1857 revolt but laid the administrative groundwork
Chronology Table for Quick Revision
| Year | Act | Key Feature | Governor-General Powers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1773 | Regulating Act | Supreme Council of Bengal; Supreme Court | Override other governors |
| 1784 | Pitt’s India Act | Dual control; Board of Control | Strengthened executive powers |
| 1793 | Charter Act | Renewal: legislative powers | Regulations over all Presidencies |
| 1813 | Charter Act | End of trade monopoly; education & religion | Expanded intervention powers |
| 1833 | Charter Act | Centralized all India powers; Law Member | Governor-General of India |
| 1853 | Charter Act | Open civil service exams | Legislative & administrative reforms |
UPSC Prelims MCQ Preparation Tips
- Focus on years and associated features
- Use elimination logic:
- Only Bengal → Regulating Act 1773
- Dual control → Pitt’s Act 1784
- All India → Charter Act 1833
- Civil service exams → Charter Act 1853
- Keep in mind key personalities:
- Warren Hastings → 1773
- Lord Cornwallis → 1786 reforms under Pitt’s Act
- Lord William Bentinck → 1833 centralization
- Practice chronology-based MCQs and feature elimination questions.
FAQs – Governor-General Acts Before 1857
Which Act first introduced the office of Governor-General?
Regulating Act of 1773.
Which act created the Board of Control in Britain?
Pitt’s India Act 1784.
Which Act centralized the Governor-General’s powers over all India?
Charter Act of 1833.
Which act introduced competitive exams for civil services?
Charter Act of 1853.
Which act ended the East India Company’s monopoly in India?
Charter Act of 1813.