In the first place, when we remember the toughest exams present in India. Besides, only one exam comes to our mind: the IAS exam. It is one of the popular exams current in India, and there are lakhs of students and working professionals applying for the exam. Further, this exam is not like any other exam, and it requires special efforts and hard work to get the best outcome in the exam. Additionally, as a part of the UPSC exam study materials, in this article, we have covered information on What is Union Territory and the difference between state and Union territory meaning. Understand all other essential details to help you with the IAS exam preparations. Read the below article and try to write done all the essentials, you can study the same during the exam. So, Let’s Begin.
- About the Article
- Historial Background
- What is Union Territory Meaning
- Union Territories in India
- Constitutional Provisions
- Composition
- Other Details
- Differences between the State and UT
- Conclusion – What is Union Territory Meaning
- FAQs – What is Union Territory Meaning
- Editor's Note | What is Union Territory

About the Article
In this article, we will be understanding the Union Territories (UTs). Further, in India, there are now eight union territories. Therefore, it is again one of the vital concepts for the UPSC exam.
Further, the State of India, which has its governments, Union Territories (UTs), are the federal territories administered by the union government of India. Besides, Puducherry and Delhi have an elected legislature and government. Currently, India has eight Union Territories.
Historial Background
Dates back to before the country’s independence. Further, areas were designated as scheduled districts in 1874. The Constitution of India was adopted in 1949, during that time, the federal structure had; Part C states which are Ajmer, Bhopal, Bilaspur, Coorg, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Cutch, Manipur, Tripura, and Vindhya Pradesh, all these were under chief commissioners’ provinces and some princely states, they are governed by a chief commissioner decided by the President of India.
Further, in the Part D states (Andaman and Nicobar Islands) administered by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central government.
What is Union Territory Meaning
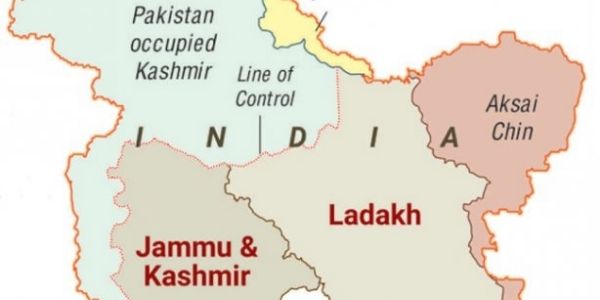
The Union Territories are the federal territories administered by the Union Government of India. Further, they are also called centrally administered territories. In the Union Territories(UTs)s, Lieutenant Governors (LGs) are appointed by the President of India. Then, the LGs serve as the UT administrators.
| Category | Federated states |
|---|---|
| Location | Republic of India |
| Number | 9 (as of 2021) |
| Populations | Lakshadweep – 64,473 (lowest); National Capital Territory of Delhi – 31,181,376 (highest) |
| Areas | 32 km2 (12 sq mi) Lakshadweep – 59,146 km2 (22,836 sq mi) Ladakh |
| Government | Union government |
| Subdivisions | Districts, Divisions |
Union Territories in India
Then currently, India has eight Union Territories (UTs) – Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Jammu, and Kashmir, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, and Puducherry. Further, in 2019, Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019. In 2020, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Diu and Daman were merged into one Union Territory (UTs) known as Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu. Besides, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 established the UTs. The Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act of 1956 introduced the notion of the UT.
| Union Territory | Capital |
|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu | Daman |
| Delhi | New Delhi |
| Jammu & Kashmir | Srinagar, Jammu |
| Ladakh | Leh, Kargil |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| Puducherry | Puducherry |
Constitutional Provisions
Further, the UTs are within Articles 239 to 241 of Part VIII of the Constitution, and their administrative system is not consistent. Besides, Article 239 of the original Constitution allowed the President to administer UTs directly through the administrators. Further, the Constitution (69th Amendment) Act, 1991 inserted Article 239AA to the Indian Constitution, which has special provisions for the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
Further, the President of India has the right to make regulations for the peace, progress, and good government of the Andaman and Nicobar, Lakshadweep Islands, Dadra, and Nagar Haveli, Daman, Diu, and Puducherry. Besides, the Indian Parliament may establish a High Court for a Union Territory by acting or proclaiming any court in any territory to be High Court. Then, the UTs are administered by the Centre through administrators. Leaving Puducherry and Delhi, none of the union territories have their parliament.
Composition
- Further, with respect to the constitutional requirements governing the makeup of the legislature in UTs, it is an decided by a body that is partially elected and partly nominated.
- Besides, a legislature that is partially elected and partly appointed will not be able to sustain democratic ideals.
- A minor change to the Government of Union Territories Act of 1963 can result in a legislature with more than half of its members being nominated. Besides, a House with a majority of appointed members cannot foster representative democracy.
Other Details
- Further, in comparision to a state the UTs have very small populations and land areas.
- Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar Islands are located far west and east of our country, respectively, and their mainland governments are quite far away, making it difficult to reach them directly through the Central government.
- Further, they are essential for India and the Indian government can act directly there in the event of an emergency.
- Besides, some of the Union Territories, such as Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu (Portuguese), Puducherry (French), and, most recently, Ladakh, have different cultures from the surrounding states.
- Further, Delhi and Chandigarh are two union territories that serve as the administrative capitals of India, Haryana, and Punjab, respectively.

Differences between the State and UT
- Then, the Indian States profits with federal relationship with the Union Government with the division of legislative. Further, with UT, it is more of a unitary relationship with the Union Government.
- States has autonomous powers while the Union Territories (UTs) do not have autonomous powers.
- A State is a consists division and has its elected government that has the rights to frame laws while a Union Territory (UTs) is a small administrative unit and is ruled by the Union Government leaving for Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Puducherry.
- Further, a Governor is the constitutional head of the State while the President of India is the executive head of the Union Territory.
| State | Union Territory |
| The state is a constituent division that has a separate government. | A Union Territory is a small administrative unit ruled by the union. |
| States are larger in size than the union territories. | UTs are much smaller in size when compared to the states. |
| The state has autonomous powers | UTs do not have independent powers |
UPSC Exam Highlights
Further, in the IAS exam, you will find three main rounds. In the first place, there will be a qualifying round that is prelims, the second stage is the main exam, and the last stage is the Interview round. Therefore, one needs to clear all stages of the IAS exam. In the IAS prelims, there are two papers, and in the IAS main exams, there are nine papers.
Suggestions for the Exam
- One must understand the IAS exam syllabus and the pattern of the paper. Further, one must refer to the previous year’s papers that will help you in many ways.
- Further, know which are the standard best books for all subjects and study from them. One cannot waste their time studying from the wrong books.
- Later, make the best use of the time and try to give time for all subjects. Try to read newspapers daily, and it will help you understand important things related to the country.
- Further, visit the official website to get the latest news related to the IAS exam.
Conclusion – What is Union Territory Meaning
To conclude, the above article speaks about the What is Union Territory. Further, we have covered all the Union Territory’s essential details that are important to understand as a part of the IAS exam. Besides, get all information related to the other UPSC exam study materials here. We have covered all the essential articles, acts, policies, and other concepts to help you with the exam preparations. Try to keep a separate book for all these and study the same during the exam. Lastly, to get the best results in the exam, one must try to cover all topics.
FAQs – What is Union Territory Meaning

What are the seven territories?
Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Chandigarh.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
Daman and Diu.
Delhi (National Capital Territory)
Lakshadweep.
Puducherry.
A-State and a Union Territory are UTs directly governed by the union government, while a separate government rules states.
Understand the IAS exam syllabus and the pattern of the paper. Further, know the standard books and try to study from them.
Editor’s Note | What is Union Territory
In brief, we have added information on one of the UPSC exam study materials is, Union Territory Meaning. Further, we have added what is the differences between the state and Union Territory. Besides, know other essential concepts related to the same like composition, operations, and other details. We have also added information about the IAS exam and some useful tips for the exam. Also, find essential links that will help you with exam preparation. In addition, one can clear the exam with the right plan and hard work. We wish you good luck with the exams.






