Supreme Court Role in Protecting Federalism: Key Constitutional Principles Explained
Federalism is one of the foundational pillars of the Indian Constitution. It ensures a balance of power between the Union and the States, preventing excessive centralization while maintaining national unity. However, Centre–State relations in India have often witnessed friction over legislative competence, administrative control, and fiscal authority.
In this constitutional framework, the Supreme Court of India plays a crucial role as the guardian of the Constitution, ensuring that federal principles are upheld and that constitutional boundaries are not transgressed. This article examines how the Supreme Court protects federalism through key constitutional provisions and judicial doctrines—making it highly relevant for GS-II Polity and UPSC Prelims.
Understanding Federalism in the Indian Constitution
Indian federalism is often described as “quasi-federal” or “cooperative federalism” due to:
- A strong Centre
- Single Constitution
- Single citizenship
- Integrated judiciary
At the same time, the Constitution clearly demarcates powers between the Union and the States, ensuring autonomy within their respective domains.
Constitutional Provisions Related to Federalism
| Article | Subject | Federal Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 246 | Legislative powers | Division of authority |
| 131 | Original jurisdiction | Neutral dispute resolution |
| 256 | Union directions | Limits executive overreach |
| 365 | Constitutional machinery | Prevents misuse |
Article 246 – Distribution of Legislative Powers
Article 246 divides legislative powers between the Union and States through:
- Union List
- State List
- Concurrent List
The Supreme Court interprets conflicts arising from overlapping subjects and ensures that legislative supremacy is exercised within constitutional limits.
Article 131 – Original Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
Article 131 empowers the Supreme Court to directly adjudicate:
- Disputes between the Union and one or more States
- Disputes between States
This provision makes the Court a neutral constitutional arbitrator in federal disputes.
Article 256 – Obligation of States
Article 256 requires States to comply with Union laws and executive directions.
The Supreme Court ensures that:
- Union directions do not become arbitrary
- State autonomy is not eroded under the guise of compliance
Article 365 – Consequences of Non‑Compliance with Union Directions
Article 365 provides that if a State fails to comply with directions given by the Union, the Centre may treat this as a situation of possible failure of constitutional machinery, which can be a ground for action under Article 356.
Judicial Review as a Tool to Protect Federalism
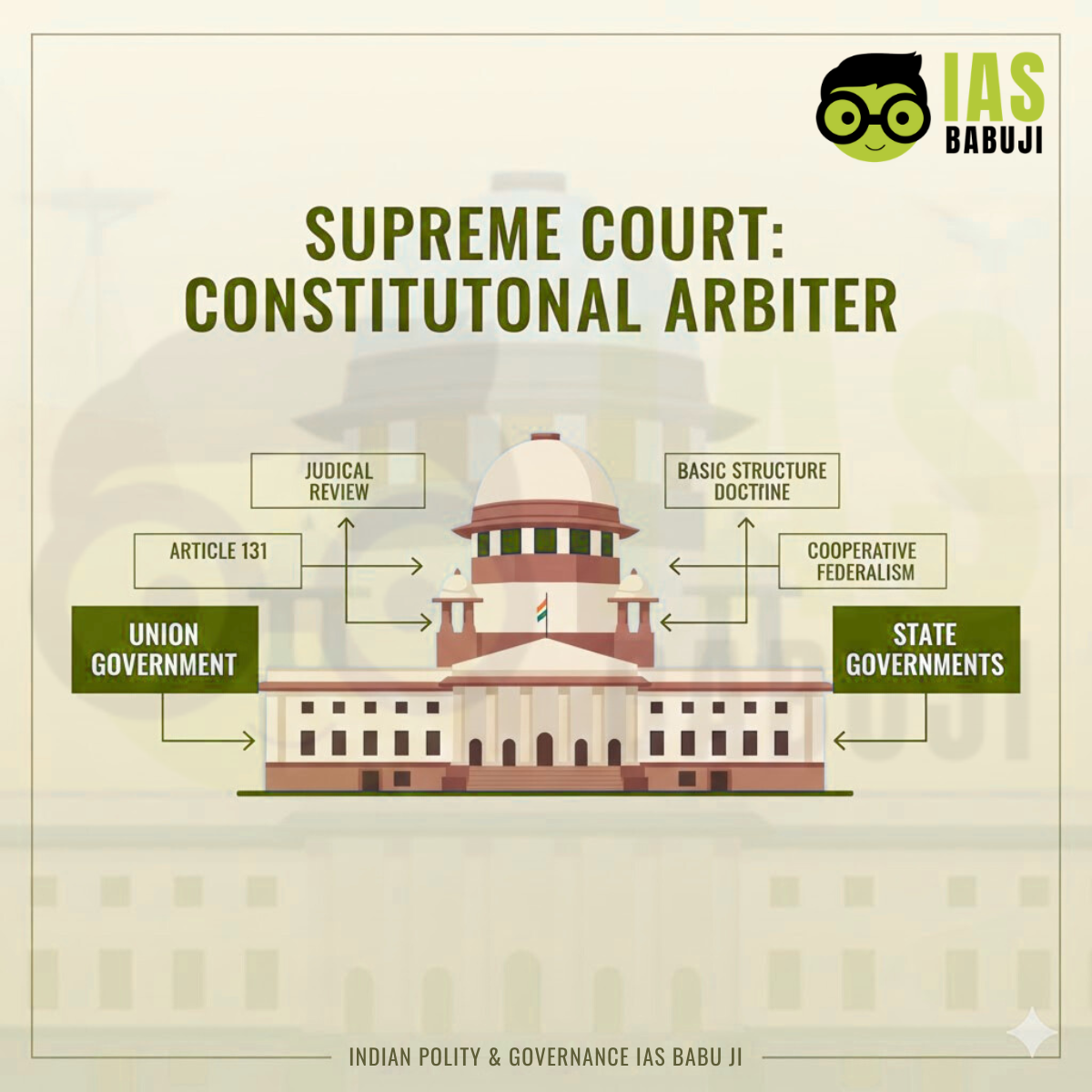
Judicial review is the most powerful mechanism through which the Supreme Court safeguards federalism.
Through judicial review, the Court:
- Examines the constitutional validity of laws
- Prevents encroachment on State powers
- Ensures adherence to the constitutional spirit
This function reinforces constitutional supremacy over political convenience.
Federalism as Part of the Basic Structure Doctrine
The Supreme Court, beginning with Kesavananda Bharati and later cases like S.R. Bommai, has held that federalism is part of the Basic Structure of the Constitution, and therefore cannot be destroyed even by a constitutional amendment.This means:
- Parliament cannot amend the Constitution in a way that destroys the federal balance
- Excessive centralization is constitutionally impermissible
This doctrine acts as a permanent constitutional safeguard against erosion of State autonomy.
Balancing Centre–State Relations Through Judicial Interpretation
Rather than promoting confrontation, the Supreme Court has often emphasized:
- Cooperative federalism
- Constitutional morality
- Dialogue-based governance
This approach strengthens federal harmony while preserving constitutional discipline.
Why This Topic Is Important for UPSC
Prelims Relevance
- Articles 131, 246, 256, 365
- Concept of federalism and basic structure
- Role of the judiciary in constitutional governance
Mains Relevance (GS-II)
- Judiciary–Executive relations
- Centre–State disputes
- Constitutional safeguards
GS-II Mains Answer (150 Words)
Q. Examine the role of the Supreme Court in protecting federalism in India.
Answer:
The Supreme Court of India plays a pivotal role in protecting the federal structure by acting as the final interpreter of the Constitution. Through Article 131, it adjudicates Centre–State and inter-State disputes, ensuring neutrality in federal conflicts. Judicial review empowers the Court to prevent legislative and executive encroachments on State powers under Article 246. Furthermore, by recognizing federalism as part of the Basic Structure, the Court has placed substantive limits on Parliament’s amending power. Judicial scrutiny of Articles 256 and 365 ensures that Union directives do not undermine State autonomy. By promoting cooperative federalism and constitutional morality, the Supreme Court preserves the delicate balance between unity and diversity, thereby strengthening India’s constitutional framework.
FAQs
Q1. Is India a federal or unitary state?
India is a federal state with a strong Centre, often described as quasi-federal.
Q2. Which Article allows Centre–State disputes in the Supreme Court?
Article 131.
Q3. Is federalism part of the Basic Structure?
Yes, federalism is part of the Basic Structure doctrine.
Q4. Why is judicial review important for federalism?
It prevents unconstitutional encroachment on State powers.
Q5. Which GS paper covers this topic?
GS-II (Polity and Governance).







