Indira Nehru Gandhi vs Raj Narain (1975): Rule of Law and Limits of Parliamentary Power
Introduction
The Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Raj Narain (1975) case is one of the most politically significant judgments in Indian constitutional history. Delivered at a critical moment in India’s democratic journey, the verdict reinforced the supremacy of the Constitution, upheld the rule of law, and placed clear limits on parliamentary power.
For UPSC aspirants, this case is essential to understand the relationship between democracy, elections, judicial review, and constitutional morality, especially in the context of the Emergency period.
Background of the Case
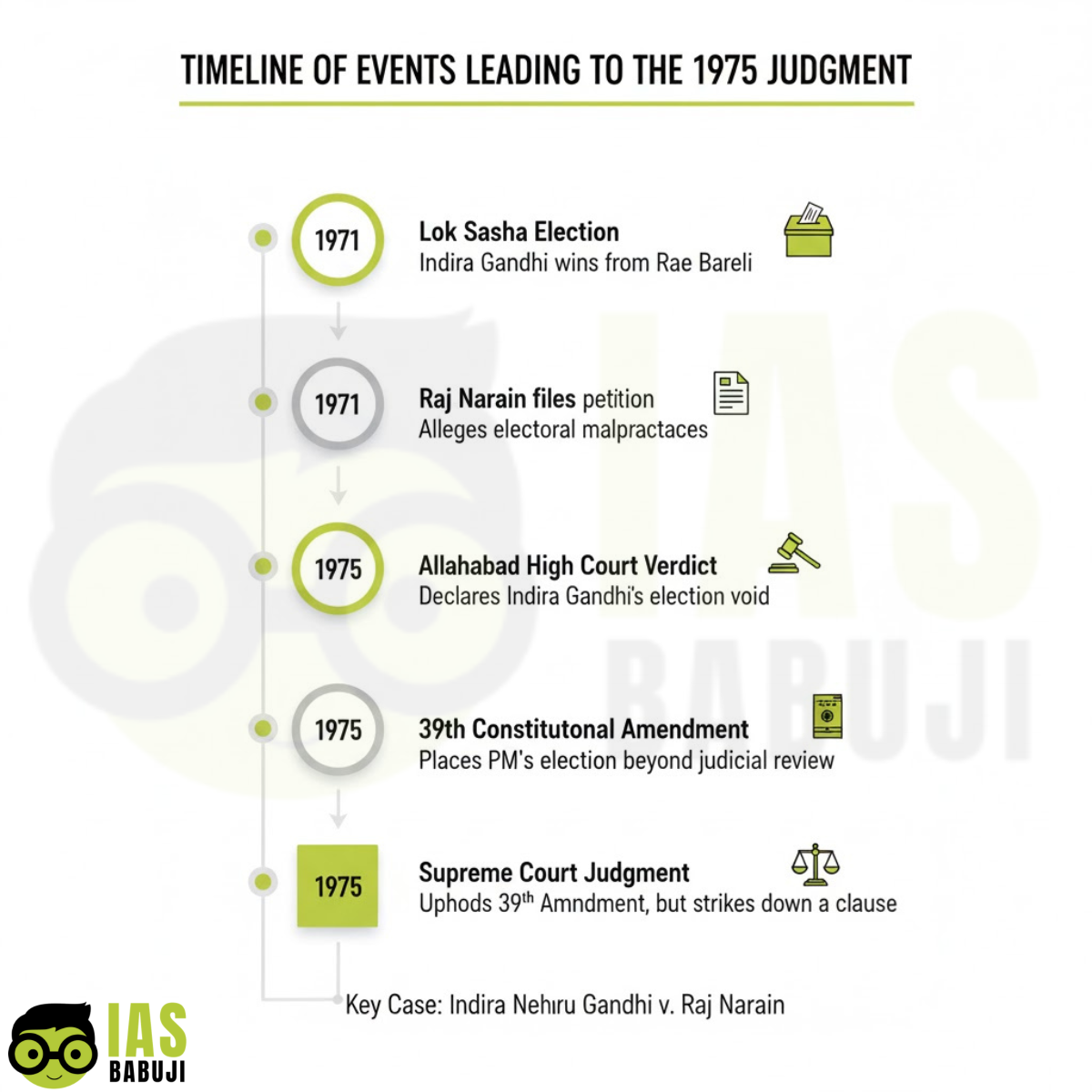
- Raj Narain challenged the election of Indira Gandhi to the Lok Sabha from Rae Bareli constituency
- He alleged misuse of government machinery and corrupt electoral practices
- The Allahabad High Court found Indira Gandhi guilty of electoral malpractice and invalidated her election in 1975
- This judgment triggered a constitutional and political crisis, leading to the declaration of an emergency
Constitutional Provisions Involved
- Article 329A – Special provisions regarding elections to Parliament
- Article 368 – Power of Parliament to amend the Constitution
- Article 14 – Equality before the law
- Article 21 – Right to life and personal liberty
Key Issues Before the Supreme Court
- Can Parliament place the election of the Prime Minister beyond judicial scrutiny?
- Does a constitutional amendment override the rule of law?
- Is a free and fair election a basic feature of the Constitution?
Supreme Court Judgment (1975)
The Supreme Court delivered a split verdict but struck down Clause (4) of Article 329A, which sought to validate Indira Gandhi’s election by removing judicial review.
Key Findings
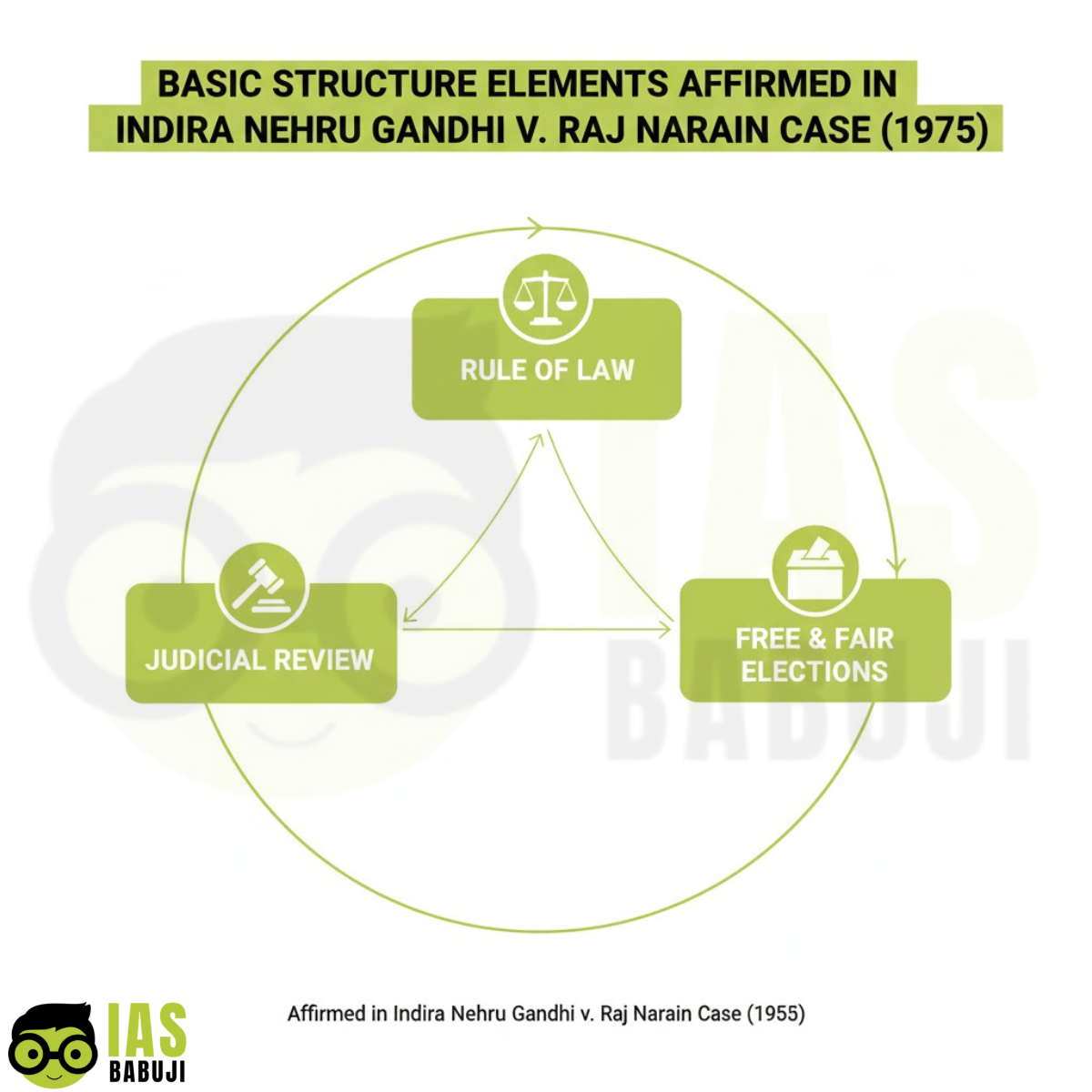
- Rule of Law is a part of the Basic Structure of the Constitution
- Judicial review cannot be excluded from election disputes
- Free and fair elections are essential for democracy
- Parliament cannot use its amending power to destroy constitutional fundamentals
Significance of the Judgment
1. Assertion of Rule of Law
- The judgment reaffirmed that no authority is above the Constitution
- Even the Prime Minister is subject to constitutional scrutiny
2. Strengthening of Judicial Review
- The Supreme Court protected its power to examine constitutional amendments
- It prevented the misuse of Parliament’s amending power
3. Protection of Democratic Values
- Elections were recognized as central to constitutional democracy
- Prevented executive dominance during the Emergency
Impact on Constitutional Jurisprudence
- Expanded the scope of the Basic Structure Doctrine
- Influenced later cases such as Minerva Mills (1980)
- Reinforced limits on Parliament’s constituent power
Criticism of the Judgment
- Some viewed it as judicial interference in political matters
- The split verdict created ambiguity on certain constitutional questions
- Critics argued it deepened executive–judiciary conflict
Despite criticism, the judgment is widely seen as a guardian of constitutional democracy.
UPSC Prelims and Mains Relevance
Prelims Focus
- Year of judgment – 1975
- Linked with the Emergency period
- Rule of Law declared part of Basic Structure
Mains (GS-II)
- Role of the judiciary in preserving democracy
- Judicial review of constitutional amendments
- Elections and constitutional morality
Essay and Ethics
- Abuse of power
- Accountability of public office holders
- Democratic governance
Previous Year Question (PYQ)
UPSC Mains 2017
“Discuss the role of the Supreme Court in maintaining constitutional balance during times of political crisis.”
This case serves as a strong example.
Conclusion
The Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Raj Narain judgment stands as a powerful reminder that constitutional supremacy and rule of law are the cornerstones of Indian democracy. Delivered during a period of political upheaval, the Supreme Court reaffirmed that democratic principles cannot be sacrificed at the altar of political convenience. By striking down provisions that sought to place elections beyond judicial scrutiny, the Court protected the integrity of the electoral process and upheld constitutional morality. For UPSC aspirants, this case highlights the judiciary’s role as a constitutional sentinel, especially during crises. Its enduring relevance lies in its affirmation that power, no matter how high, remains accountable under the Constitution.
FAQs on Indira Nehru Gandhi vs Raj Narain (1975)
Q1. Why is the Indira Gandhi v. Raj Narain case important for UPSC?
It established the Rule of Law and free elections as part of the Basic Structure.
Q2. Which constitutional amendment was challenged in this case?
The 39th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1975.
Q3. What was Article 329A related to?
It dealt with election disputes involving high constitutional authorities.
Q4. Which doctrine was strengthened by this case?
The Basic Structure Doctrine.