S.R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994): Federalism and Limits of Article 356
Introduction
The S.R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994) case is a landmark Supreme Court judgment that transformed the interpretation of Article 356 (President’s Rule) and strengthened the federal structure of India. Delivered in response to repeated misuse of central power, the judgment placed constitutional checks on arbitrary dismissal of state governments.
For UPSC aspirants, this case is essential for understanding Centre–State relations, federalism, constitutional morality, and judicial review.
Background of the Case
- S.R. Bommai was the Chief Minister of Karnataka
- His government was dismissed in 1989 under Article 356
- The dismissal was based on the Governor’s report claiming loss of majority
- The proclamation was challenged before the Supreme Court along with similar cases from other states
Constitutional Provisions Involved
- Article 356 – Proclamation of President’s Rule
- Article 355 – Duty of the Union to protect states
- Article 74 – Aid and advice of the Council of Ministers
- Article 164 – Collective responsibility of the Council of Ministers
Key Issues Before the Supreme Court
- Can the President’s satisfaction under Article 356 be judicially reviewed?
- Is the Governor’s report immune from scrutiny?
- What is the correct test to determine loss of majority in a state government?
Supreme Court Judgment (1994)
A nine-judge Constitution Bench delivered a unanimous and detailed judgment limiting arbitrary use of Article 356.
Key Findings
- President’s Rule is subject to judicial review
- The majority of a government must be tested on the floor of the House, not by the Governor
- Secularism is part of the Basic Structure of the Constitution
- If a proclamation is unconstitutional, the dismissed government can be restored
Guidelines Laid Down by the Court
The Court laid down clear constitutional safeguards:
- The floor test is the primary method to determine the majority
- Governor’s report is not final or binding
- Article 356 is an exceptional provision, not a routine tool
- Courts can examine the material on which the President’s satisfaction is based
Significance of the Judgment
1. Strengthening Federalism
- Reduced arbitrary interference by the Centre
- Protected autonomy of state governments
2. Judicial Control over Executive Power
- Established that executive discretion is not absolute
- Reinforced constitutional accountability
3. Protection of Democratic Norms
- Prevented misuse of the Governor’s office
- Upheld elected governments
Impact on Centre–State Relations
- Decline in misuse of President’s Rule after 1994
- Shift towards cooperative federalism
- Influenced later practices and conventions involving Governors
Criticism of the Judgment
- Some argue that it has judicialised political questions
- Implementation depends heavily on judicial intervention
- Concerns over the delay in judicial review during political crises
Despite criticism, the judgment is widely regarded as a turning point in Indian federalism.
UPSC Prelims and Mains Relevance
Prelims Focus
- Year – 1994
- Article 356 and President’s Rule
- Secularism as part of the Basic Structure
Mains (GS-II)
- Centre–State relations
- Role of the judiciary in the federal balance
- Governor’s discretion and accountability
Essay and Ethics
- Abuse of power
- Constitutional morality
- Federal democracy
Conclusion
The S.R. Bommai judgment marked a decisive shift towards constitutional federalism by curbing arbitrary use of President’s Rule. By subjecting presidential proclamations to judicial review and emphasizing floor tests as the sole democratic method to assess majority, the Supreme Court strengthened democratic accountability and state autonomy. The ruling also elevated secularism to the status of a Basic Structure principle, reinforcing India’s pluralistic constitutional identity. For UPSC aspirants, this case serves as a classic example of how judicial intervention can restore constitutional balance and protect democratic institutions. Its enduring relevance lies in its clear message that federalism and democracy cannot be compromised for political convenience.
FAQs on S.R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994)
Q1. Why is the S.R. Bommai case important for UPSC?
It limited misuse of Article 356 and strengthened federalism.
Q2. What key principle was established regarding majority testing?
Majority must be proven on the floor of the House.
Q3. Which constitutional value was declared part of Basic Structure?
Secularism.
Q4. Can courts restore dismissed state governments?
Yes, if the President’s Rule is found unconstitutional.
Infographic Prompts (With Placement)
Infographic 1 – After Guidelines Section
Title: When Can Article 356 Be Applied
Prompt:
Flowchart infographic showing constitutional conditions for President’s Rule, including Governor’s report, floor test, and judicial review. Clean academic style, white background, accent color #b3c839.
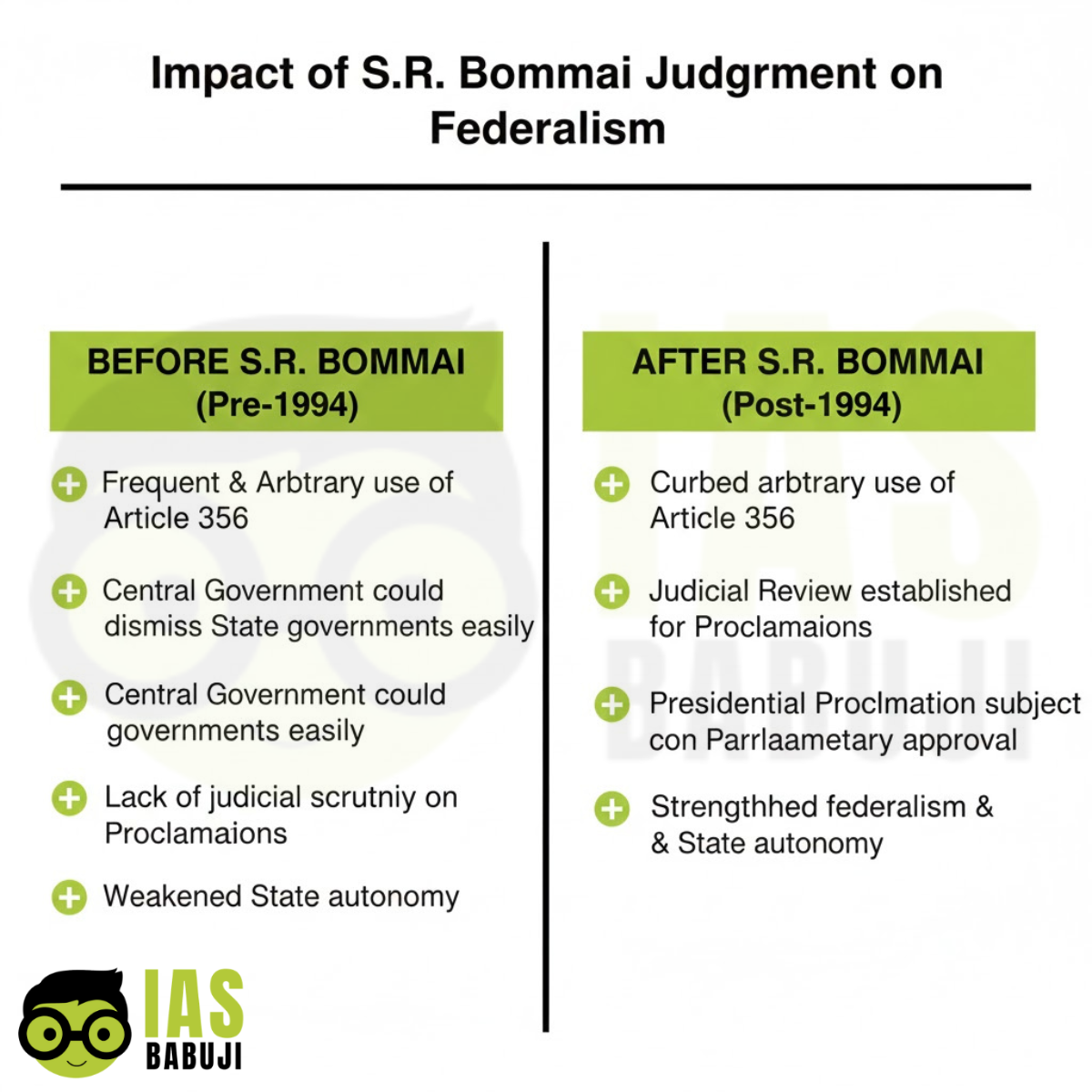
Infographic 2 – Before Conclusion
Title: Impact of S.R. Bommai Judgment on Federalism
Prompt:
Comparison infographic showing Centre–State relations before and after 1994. Minimal academic layout, accent color #b3c839.
Feature Image Prompt (3D Illustrator)
Prompt:
A 3D isometric illustration of the Supreme Court of India protecting a state assembly with a constitutional shield, Parliament in the background, clean academic style, white background, theme color #b3c839.
Next bolo:








