Monetary Policy vs Fiscal Policy: Which Is More Effective During Economic Slowdown?
Introduction
Economic slowdowns pose a serious challenge to governments and central banks, requiring timely and effective policy intervention. In India, two primary macroeconomic tools are used to revive growth: monetary policy managed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and fiscal policy executed by the government. While both aim to stabilise the economy, their effectiveness during a slowdown often becomes a subject of debate. Understanding their relative strengths, limitations, and ethical dimensions is crucial for UPSC aspirants, particularly for GS Paper III, GS Paper IV, and essay writing.
Understanding Economic Slowdown
An economic slowdown refers to a phase of reduced growth characterised by:
- Decline in investment and industrial output
- Weak consumer demand
- Rising unemployment
- Lower tax revenues
Policy response during such phases must balance growth revival with macroeconomic stability.
Monetary Policy: Role During Economic Slowdown
What is Monetary Policy?
Monetary policy involves the regulation of money supply and credit conditions by the RBI to achieve price stability and support growth.
Key Monetary Tools
- Repo rate and reverse repo rate
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
- Open Market Operations (OMO)
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF)
Effectiveness During Slowdown
- Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and investment
- Improves liquidity in the banking system
- Boosts consumption through cheaper credit
Limitations
- Weak transmission due to the stressed banking sector
- Ineffective when demand is already depressed
- Cannot directly address structural or supply-side issues
Fiscal Policy: Role During Economic Slowdown
What is Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy refers to government decisions on taxation, expenditure, and borrowing to influence economic activity.
Key Fiscal Instruments
- Increased public expenditure
- Tax cuts and incentives
- Welfare and employment schemes
- Capital investment in infrastructure
Effectiveness During Slowdown
- Direct impact on demand and employment
- Counter-cyclical role through deficit spending
- Strong multiplier effect in developing economies
Limitations
- High fiscal deficit may raise debt sustainability concerns
- Risk of inflation if overused
- Implementation delays and inefficiencies
Monetary Policy vs Fiscal Policy: A Comparative Analysis
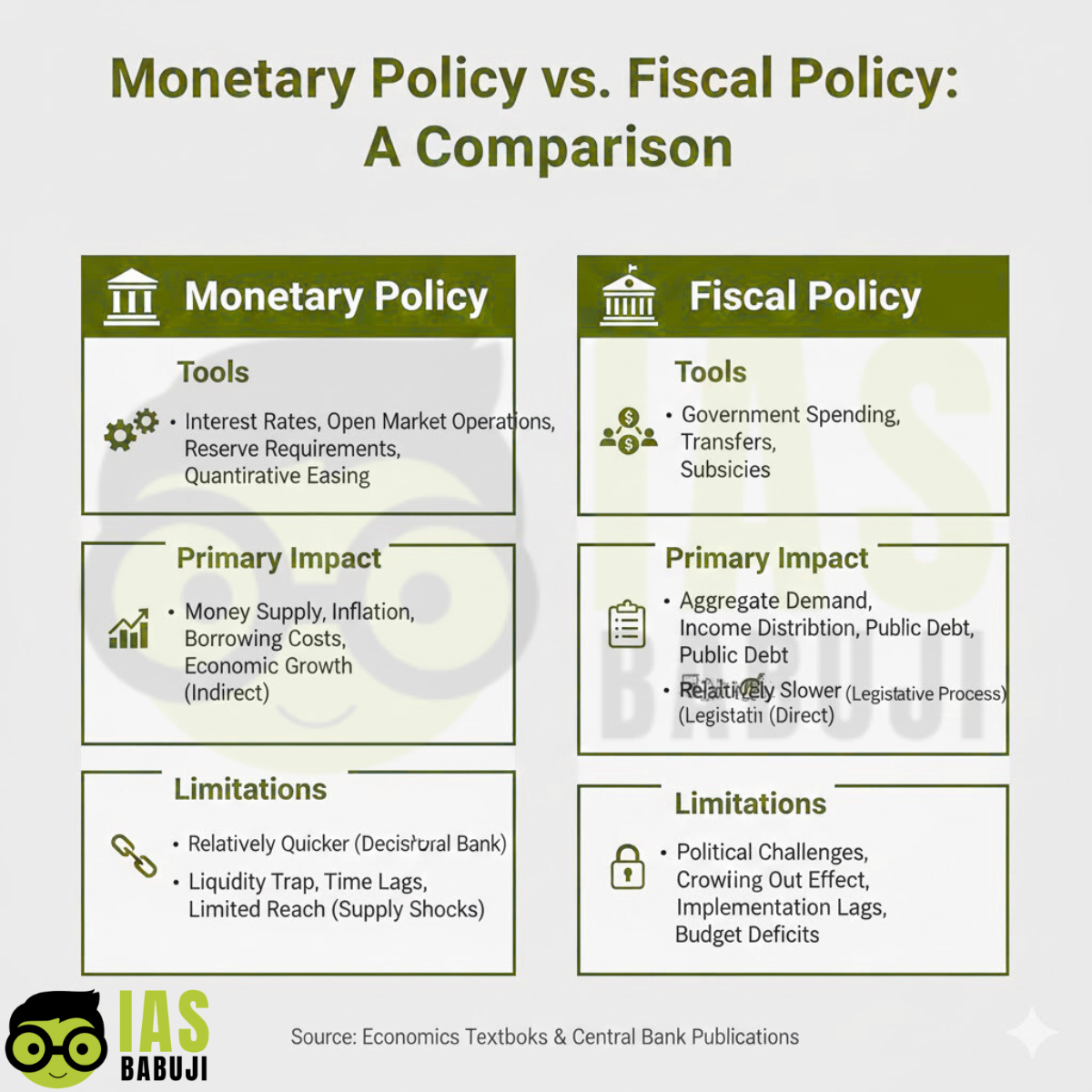
-
Speed of Implementation
-
Monetary policy is quicker to deploy
-
Fiscal policy involves budgetary and administrative delays
-
-
Targeting
-
Monetary policy is indirect and market-driven
-
Fiscal policy can be targeted towards specific sectors
-
-
Impact on Demand
-
Fiscal policy has a stronger demand-side impact
-
Monetary policy works mainly through credit channels
-
-
Institutional Accountability
-
Monetary policy operates through an independent RBI
-
Fiscal policy is accountable to Parliament
-
Which is More Effective During a Slowdown?
In the Indian context, fiscal policy tends to be more effective during severe slowdowns due to:
- Large informal sector
- Credit constraints
- High unemployment elasticity
However, fiscal policy alone cannot sustain recovery without supportive monetary conditions.
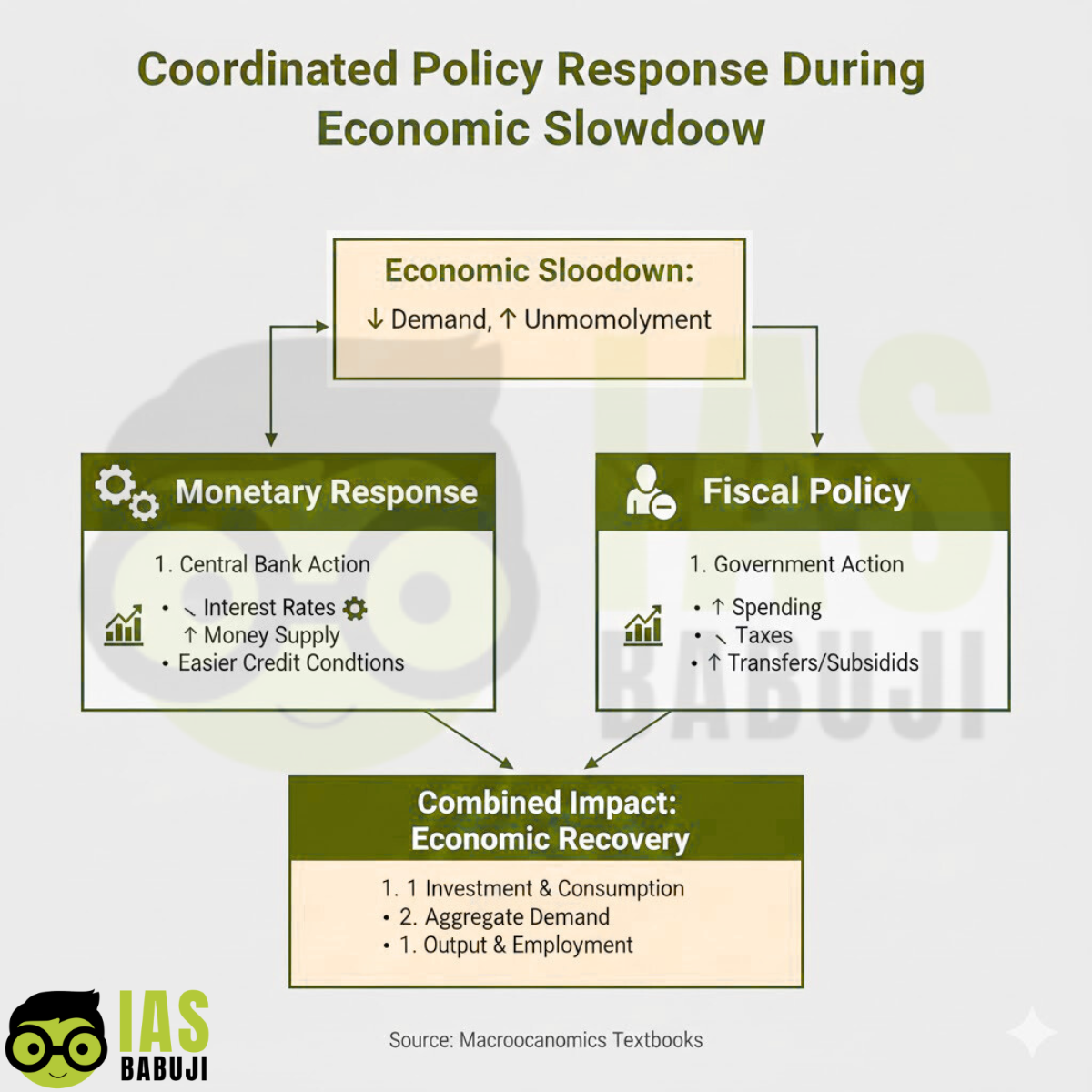
Need for Monetary–Fiscal Coordination
- Loose monetary policy complements fiscal stimulus
- Prevents crowding out of private investment
- Enhances overall policy effectiveness
Economic revival requires synergy, not competition, between the two.
Ethical and Governance Dimensions
Ethical Considerations
- Fiscal policy reflects distributive justice and welfare ethics
- Monetary policy emphasises price stability and intergenerational equity
Governance Challenges
- Risk of fiscal populism
- Maintaining central bank independence
- Transparency and accountability in public spending
A balanced approach upholds constitutional morality and public interest.
Indian Experience and Lessons
- Pandemic response highlighted fiscal dominance supported by accommodative monetary policy
- Infrastructure-led fiscal spending supported recovery
- RBI ensured liquidity and financial stability
This experience underscores the importance of coordinated policy action.
Way Forward
- Strengthening fiscal capacity without compromising sustainability
- Improving monetary transmission
- Institutionalising policy coordination frameworks
- Focusing on long-term structural reforms
Conclusion
During an economic slowdown, the debate between monetary and fiscal policy should not be framed as a binary choice. While monetary policy provides quick liquidity support and stabilises financial markets, fiscal policy plays a decisive role in reviving demand, creating employment, and addressing structural weaknesses. In a developing economy like India, fiscal policy tends to be more effective during deep slowdowns, especially when private investment and consumption remain subdued. However, excessive reliance on fiscal expansion can strain public finances and undermine long-term stability. Therefore, the most effective strategy lies in coordinated monetary–fiscal action, guided by ethical governance, institutional accountability, and macroeconomic prudence. Such a balanced approach ensures sustainable recovery while safeguarding economic and social welfare.
FAQs on Which Is More Effective During an Economic Slowdown?
Which policy is more effective during a recession?
Fiscal policy is generally more effective due to its direct impact on demand and employment.
Can monetary policy alone revive growth?
Monetary policy alone is insufficient during deep slowdowns with weak demand.
Why is coordination between the RBI and the government important?
Coordination ensures effective policy transmission and macroeconomic stability.
Which UPSC papers cover this topic?
GS Paper III, GS Paper IV, and Essay.
SEO Meta Data
Meta Title:
Monetary Policy vs Fiscal Policy During Economic Slowdown | UPSC GS III
Meta Description:
Tags (comma-separated)
Monetary Policy, Fiscal Policy, Economic Slowdown, Indian Economy, RBI, UPSC GS III Economy, Economic Governance, Ethics in Policy Making







