GS Paper II has many topics. It is a wide subject. Moreover, the subject can fetch you good marks. Normally, students use the Indian Polity book by M. Laxmikanth. You will find a section with the List of Constitutional Bodies/Posts & Chart Important for UPSC in India. This topic is crucial to cover for your prelims paper. Moreover, you will also need this one in your main paper. Further, if you opt for a public admin optional paper, covering this topic is very imp. How will reading about this topic help you in your UPSC prep? Let us answer this. Being a UPSC aspirant, you need to know the 360-degree view of a topic. When you first open your study material, you will learn about the basic components of the polity. Secondly, you will read about the various institutions of India. For example, the parliament, judiciary, etc.
About Constitutional Bodies in India
All these pillars play a very key role in governance. They are the pillars that support our nation. But can only the three key pillars support a nation of billions? The answer is no. We know that there is a need for support organizations. Hence, a lot of other bodies support the countries admin and polity. There are statutory bodies to support the govt. These are created by-laws or statutes. Hence, the name statutory bodies. Secondly, some bodies are already mentioned in the constitution. These bodies are the Constitution Bodies Important for UPSC in India. We will list them further in this article. They are validated by our country’s original legal text. Hence, the opinion of a constitutional body is highly held by others.
Reading about this topic, you will come across the following sub-topics. Firstly, you will read about the basic intro of the body. Secondly, you will read about the amendment or any other provision that led to its birth. Thirdly, you will study the members of the body. Then, you will come across the features of the body. Further, you will read about what exactly the constitutional body does. (Not necessarily in this order). Hence, you will learn about the purpose of its formation. In addition to this, you will study how the members of the body face removal from office. You will also read about their setbacks, role, and freedom to function. There are around 12 bodies in the list of constitutional bodies of India. We will list them down. Further, we will also read about the constitutional posts in India and chart details.
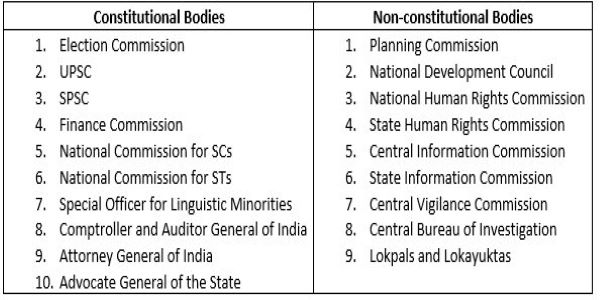
List of Constitutional Bodies
Here are is the list of the imp bodies for UPSC.
- Election Commission.
- UPSC.
- SPSC.
- Finance Commission.
- GST Council.
- National Commission for SCs.
- National Commission for STs.
- CAG of India.
- Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities.
- National Commission for BCs.
- Attorney General of India.
- Advocate General of the State.
As we saw, there are many bodies. Reading about each of them is tough. Hence, many aspirants prefer to use a constitutional bodies chart. These charts help them to memorize all the details in short. Moreover, it is stored in their head for a long time. Further in this article, we will read about the functions of these bodies. We will also read about their composition.
Constitutional Posts in India of Different Bodies
Firstly, let us talk about the election commission. This body comes under article 324. The constitutional posts in India under this body are that of the CEC. CEC stands for the Chief Election Commissioner. In addition to this, the body also has few other officers. The tenure of members is 6 years or 65 years, whichever is earlier. The members are eligible for further appointments as well. The body is responsible for the conduct of free and fair elections in the country. They register political parties. Moreover, they monitor the elections as well. To read more about the EC: click here.
Secondly, let us talk about the Attorney General of India. This body is listed in the 76th article. It is also available in the Constitutional bodies/posts chart in India. The attorney general doesn’t have a fixed tenure. President’s pleasure decides his tenure. The post holder enjoys the privileges of an MP. He has a right to an audience in all Indian courts. Further, he can attend both the houses of the parliament. However, he does not have the vote in any of them.
CAG and The Finance Commission of India
Next, let us look at the CAG office. This constitutional body is listed in the 148th article. The tenure of CAG is 6 years or 65 years, whichever is earlier. The removal process for this office is the same as that of an SC judge. The CAG cannot hold any other officer thereafter. The CAG is the national auditor. Hence, he audits the various govt funds. He also advises the president in such matters as the audit. Further, let us talk about the Constitutional Posts of the Finance Commission of India. The body is listed in article number 280. It has a chairman and four other members. The body decides the tax sharing b/w the center and states. It refers to financial matters to the President. It also divides resources for the local govt. This body has the powers of a civil court in financial matters.
National Commissions
Next, we will talk about the other Constitutional Bodies/Posts Important for UPSC in India from the chart. We will talk about the National Commissions for SCs/STs/OBCs. The NCSC is listed in article number 338. The NCST is listed in article number 338 A. Further, article 338 B is for NCOBC. They have a similar composition. Moreover, the functions are also quite similar. These bodies have a chairman and a vice-chairman. Moreover, there are 3 constitutional posts in India for each of these commissions. They are quasi-judicial bodies. They ensure that the safeguards for SC/ST/OBCs are properly implemented. Moreover, they enjoy the powers of a civil court.
Special Linguistic Minorities Officer, UPSC, GST Council
Next, let us talk about the special officer for linguistic minorities. This body is listed in article 350 B. There are 3 imp constitutional posts of India under this body. Firstly, there is a commissioner, a deputy commissioner, and an asst. commissioner. The tenure and removal are based don’t the President’s pleasure. Further, it works for the protection of linguistic minorities. After this, let us discuss UPSC from the list of the constitutional bodies/posts in India. Article 315 to Article 323 talks about this body. There are around 9 to 11 members in this body.
The members enjoy a tenure of 6 years or 65 years, whichever is earlier. The chairman of UPSC doesn’t enjoy the second appointment. The other members can be appointed at SPSC or UPSC. They recruit civil service members. The same applies to the SPSC. However, the tenure is 6 years or 62 years, whichever is earlier. Next, we will discuss the GST council. This is one of the latest addition to the list of constitutional bodies in India. Article number 279 A talks about this body. The finance minister chairs this body. Union ministers of state in charge of revenue or finance are also members of this body. It also has a Minister of Finance from each state as a member. The council administers the GST implementation in the country.
Finally, let us discuss the last body on the list. That is the Advocate General of State. Article 165, 177, and 194 talks about this office. He advises the state govt in legal matters. The constitution lets the advocate general of the state administer legal matters of the state. For more such articles: click here.
FAQs
As per the list of constitutional bodies/posts in the India chart, there are 12 bodies. However, the parliament can make amendments to the text and add new ones. The GST council is a very recent addition to the list.
A chart lists all the constitutional bodies on a single piece of paper. Usually, you can find these charts online or in local stores. Sometimes you can also get the chart with a world map.
Every constitutional body is important for UPSC. You need to browse through each one of them at least twice during your prep. Further, you need to stress more on UPSC, FC, National commissions, the attorney general of India, CAG, and EC.
Editor’s Note | Constitutional Bodies in India
Here, we will conclude our article. Today we read about the list of constitutional bodies in India. We discussed the use of a chart in studying this topic. Further, we talked about the importance of these bodies in our governance. After this, we spoke about the composition of these bodies. Thus, we learned about the constitutional posts in India. As per this, there is a chairman for every legal body. Moreover, there are also some other members to support the admin. After this, we also listed their powers and functions in our country. Thus, we read about some of the most imp posts in India. That is CAG, CEC, Finance commissioner, etc. We hope that this article helps you in collecting the necessary details for your UPSC prep.