Role of Empathy in Public Service Delivery: A Pillar of Humane Administration
Introduction
Public service delivery is not merely about implementing laws, schemes, and policies; it is about serving people, especially the most vulnerable sections of society. In this context, empathy becomes a foundational ethical value for civil servants. Empathy enables administrators to understand the feelings, hardships, and lived realities of citizens, thereby improving both the quality and effectiveness of governance. In a diverse and unequal society like India, empathy-driven administration is essential for ensuring justice, inclusiveness, and trust in public institutions.
Understanding Empathy in Public Administration

Empathy refers to the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, while maintaining objectivity and professional responsibility.
Key dimensions:
- Cognitive empathy: Understanding the problems faced by citizens
- Emotional empathy: Sensitivity towards suffering and distress
- Administrative empathy: Translating understanding into humane policy implementation
Empathy does not mean emotional decision-making; it means informed, people-centric governance.
Why Empathy Matters in Public Service Delivery
Improves Policy Implementation
- Helps officials understand ground realities
- Reduces rigid and mechanical application of rules
- Enhances the effectiveness of welfare schemes
Strengthens Trust Between State and Citizens
- Citizens feel heard and respected
- Improves the legitimacy of institutions
- Reduces grievance and conflict
Enhances Equity and Inclusion
- Addresses the needs of marginalized groups
- Ensures last-mile delivery
- Prevents exclusion due to procedural rigidity
Empathy vs Sympathy in Governance
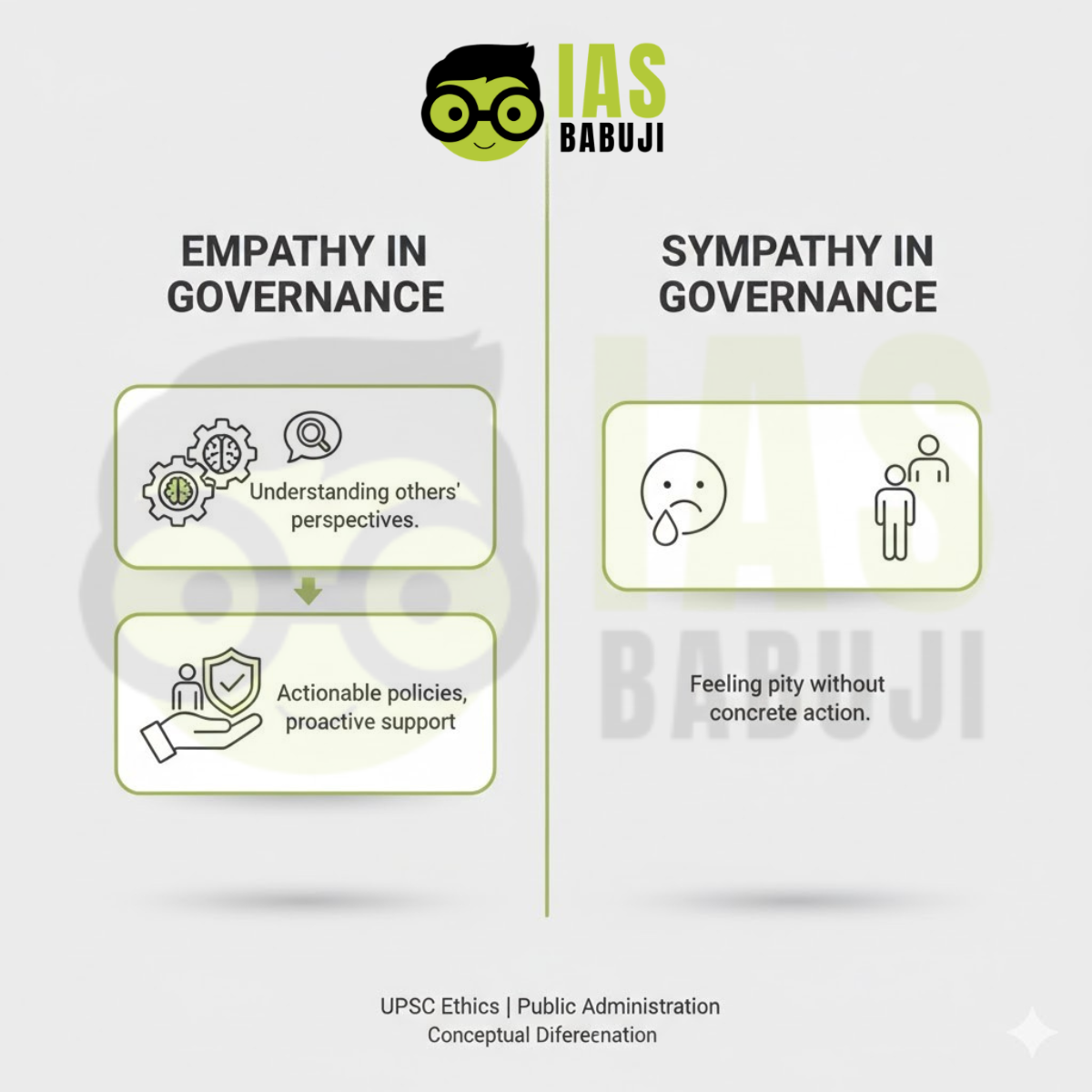
It is important to distinguish between empathy and sympathy.
- Sympathy involves feeling pity, often passive
- Empathy involves understanding and action
Public servants require empathy, not sympathy, to balance compassion with constitutional duty.
Empathy as a Tool for Ethical Governance

Ethical principles supported by empathy:
- Justice: Fair treatment based on real needs
- Compassion: Humaneness in decision-making
- Accountability: Responsibility towards citizens
- Integrity: Acting in public interest
Empathy ensures that governance remains value-based rather than rule-bound alone.
Role of Empathy in Key Areas of Public Service

Welfare Schemes
- Understanding barriers faced by beneficiaries
- Simplifying procedures
- Preventing exclusion errors
Law and Order Administration
- Humane policing
- Respect for human rights
- Conflict-sensitive governance
Disaster Management
- Prioritizing relief over procedure
- Sensitivity towards trauma victims
- Inclusive rehabilitation efforts
Service Delivery at Cutting Edge Level
- Role of frontline workers
- Compassionate interaction with citizens
- Reduction of harassment and corruption
Empathy in Indian Administrative Tradition
Indian civil services emphasize values such as:
- Service before self
- Public welfare as the supreme law
- Ethical leadership
Reforms and training modules increasingly stress emotional intelligence and ethical competence.
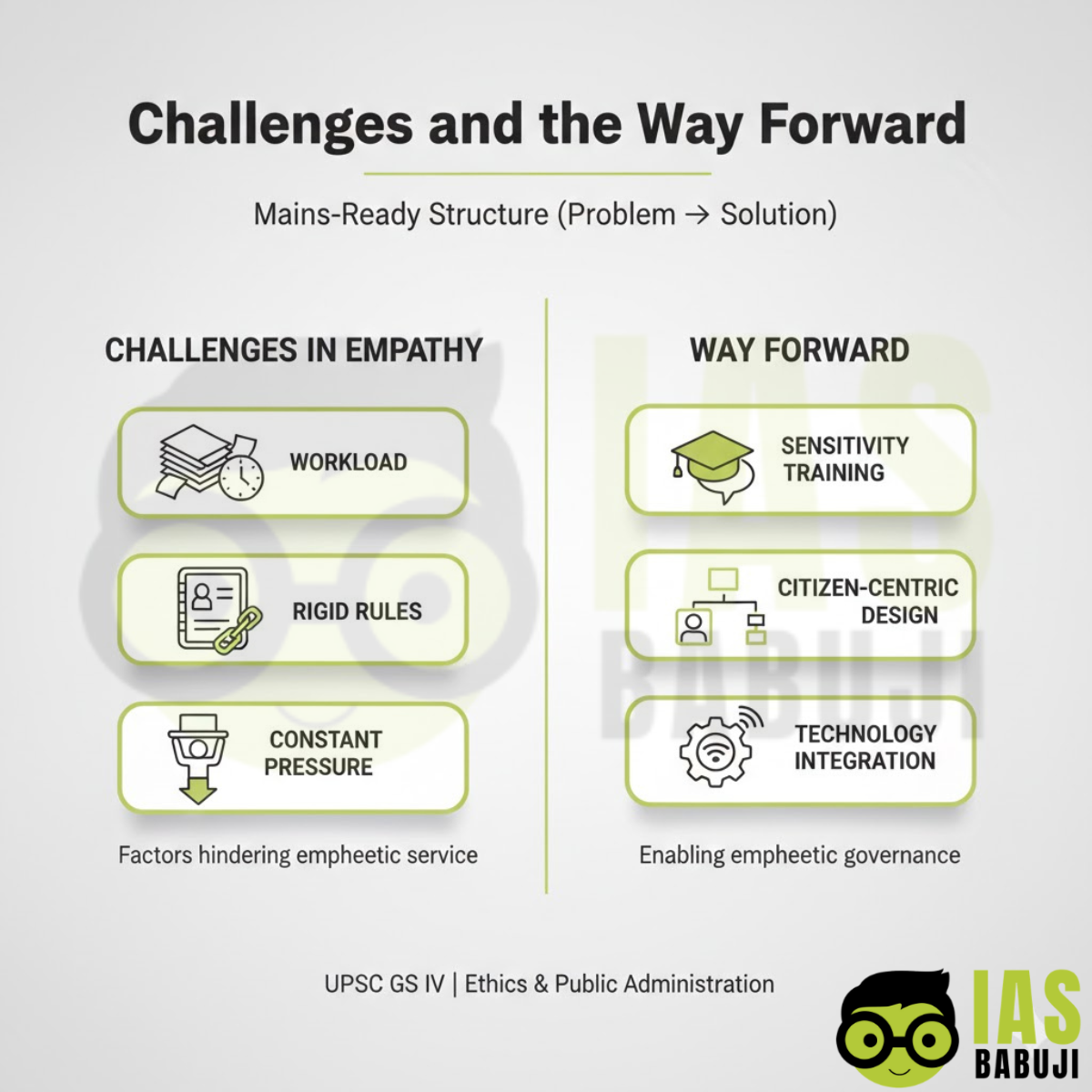
Challenges in Practicing Empathy
- Excessive workload and staff shortages
- Rule-bound bureaucratic culture
- Fear of discretion misuse
- Political and institutional pressures
Empathy must be institutionalized rather than left to individual goodwill.
Balancing Empathy with Objectivity
Empathy should not lead to:
- Bias or favoritism
- Violation of the law
- Arbitrary decision-making
Hence, empathy must operate within constitutional and legal frameworks.
Way Forward
- Ethics training in civil services
- Citizen-centric service design
- Sensitization of frontline officials
- Use of technology to reduce harassment
- Performance evaluation linked to service quality
Empathy should be seen as an administrative skill, not a weakness.
Conclusion
Empathy plays a critical role in enhancing the quality, fairness, and effectiveness of public service delivery. In a country marked by socio-economic diversity and inequality, empathetic governance ensures that policies are implemented with sensitivity to ground realities rather than through rigid proceduralism. Empathy strengthens trust between citizens and the State, improves inclusion, and upholds the ethical foundations of public administration. However, empathy must be balanced with objectivity, legality, and accountability to prevent misuse of discretion. Institutionalizing empathy through training, evaluation, and organizational culture is essential for ethical governance. Ultimately, empathy transforms public administration from mere rule enforcement into meaningful public service, aligning governance with constitutional values of justice, dignity, and welfare.
FAQs
What is empathy in public service delivery?
Empathy in public service delivery refers to the ability of public officials to understand the needs, emotions, and lived realities of citizens and reflect this understanding in humane, fair, and effective policy implementation.
Why is empathy important for civil servants?
Empathy helps civil servants connect policies with ground realities, improves inclusiveness, strengthens trust between citizens and the State, and ensures ethical and people-centric governance.
How is empathy different from sympathy in governance?
Empathy involves understanding citizens’ problems and taking appropriate action within the law, whereas sympathy is limited to emotional concern without administrative responsibility or corrective action.
Can empathy lead to bias or misuse of discretion?
If not balanced with objectivity and legality, empathy may lead to favoritism. Therefore, empathy must operate within constitutional values, rules, and accountability mechanisms.
How does empathy improve welfare scheme implementation?
Empathy helps administrators identify exclusion errors, simplify procedures, understand beneficiary constraints, and ensure effective last-mile delivery of welfare schemes.
Is empathy relevant in law and order administration?
Yes. Empathetic policing promotes human rights, conflict-sensitive responses, and community trust while maintaining public order and rule of law.
How can empathy be institutionalized in public administration?
Through ethics training, emotional intelligence modules, citizen-centric service design, performance evaluation based on service quality, and use of technology to reduce harassment.
Which UPSC paper covers empathy in public service delivery?
Primarily GS Paper IV (Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude). It is also relevant for Essay paper and ethics-based case studies.
Can empathy be used in UPSC case study answers?
Yes. Empathy is a high-scoring ethical value and can be used to justify balanced decisions, humane alternatives, and citizen-oriented solutions in GS IV case studies.
How does empathy support good governance?
Empathy ensures responsive, inclusive, transparent, and accountable governance by aligning administrative actions with citizens’ real needs and constitutional values.







